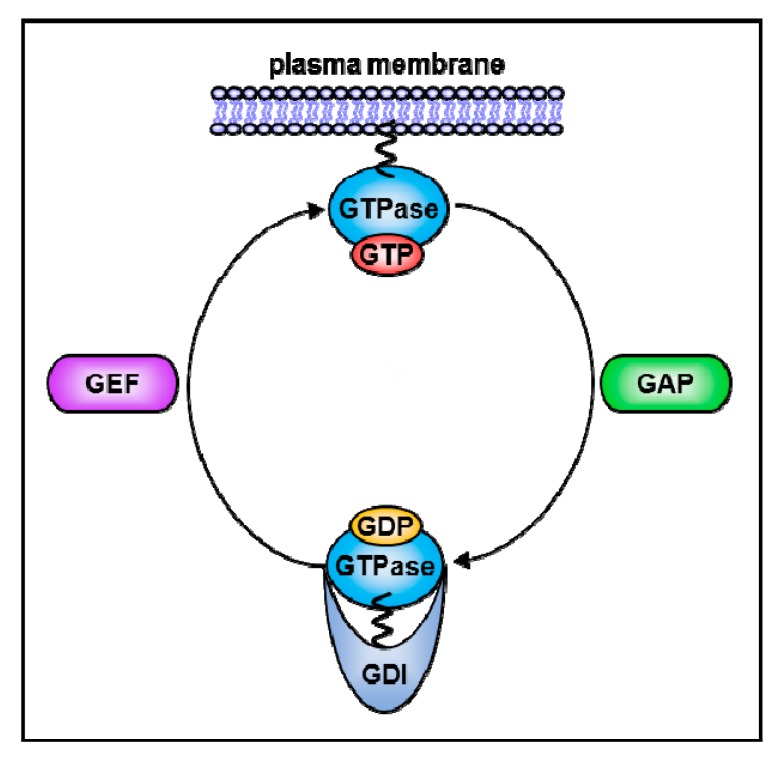
Figure 1.
The regulation of Rho GTPases by GEPs, GAPs, and GDIs. GEFs bind to GDP-bound RhoGTPases and promotes the exchange of GDP for GTP, thereby activating RhoGTPases. GAPs bind to GTP-bound RhoGTPases and catalyze the exchange of GDP for GTP, thereby inactivating RhoGTPases. The N-terminal domain of RhoGDIs binds to switch I and II domains of RhoGTPases. The C-terminal region of RhoGDIs forms a hydrophobic pocket and binds to prenylated RhoGTPases. Therefore, RhoGDIs can extract RhoGTPases from plasm membrane by binding the isoprenoid moiety and sequester them away in the cytoplasmic compartment.