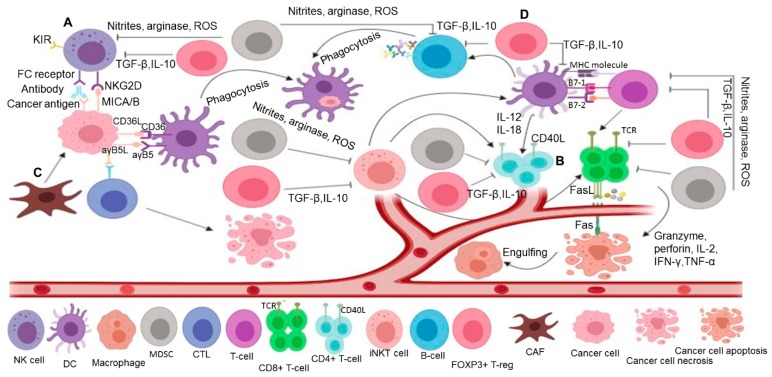
Figure 4.
The role of immune cells in cancer development. (A) NK cells are the first line of innate immunity, activated by NKG2D and CD16 (Fc receptor) to promotes cancer cell killing through an antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC effect). (B) The activation of CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and B cells promotes phagocytosis of cancer cells by dendritic cells and macrophages through Fas/FasL, granzymes, perforins, interleukin-2 (IL-2), tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), and interferon –γ (IFN-γ). (C) Cancer associated fibroblast (CAF) provides support for cancer cells to promotes immune escape. (D) By contrast, these anti-tumor function is counteracted by the presence of fork head box P3 (FOXP3+) T regs (regulatory T cell) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) through production of TGF-β, IL-10, arginase, nitrites and ROS.