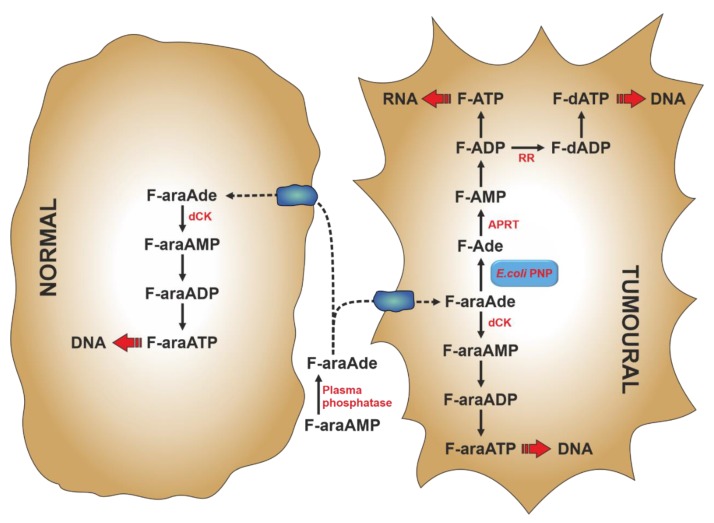
Figure 4.
Metabolism of F-araAMP in normal and tumoural cells subjected to Escherichia coli PNP (ePNP)/F-araAMP GDEPT. 9-β-arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoroadenosine 5’-monophoaphate (F-araAMP) is cleaved by plasma phosphatases into 9-β-arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoroadenine (F-araAde), which enters both normal and tumoural cells. Inside the cell, it is activated to the monophosphate by cellular deoxycytidine kinase (dCK). In tumour cells, the presence of ePNP allows for an additional activation pathway, which proceeds through a phosphorolytic cleavage to give 2-fluoroadenine (F-Ade), which is activated by cellular adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT). Through the action of ribonucleotide reductase (RR), F-ADP is converted to the respective deoxynucleotide, thus interfering also on DNA synthesis. GDEPT: gene-directed enzyme prodrug therapy.