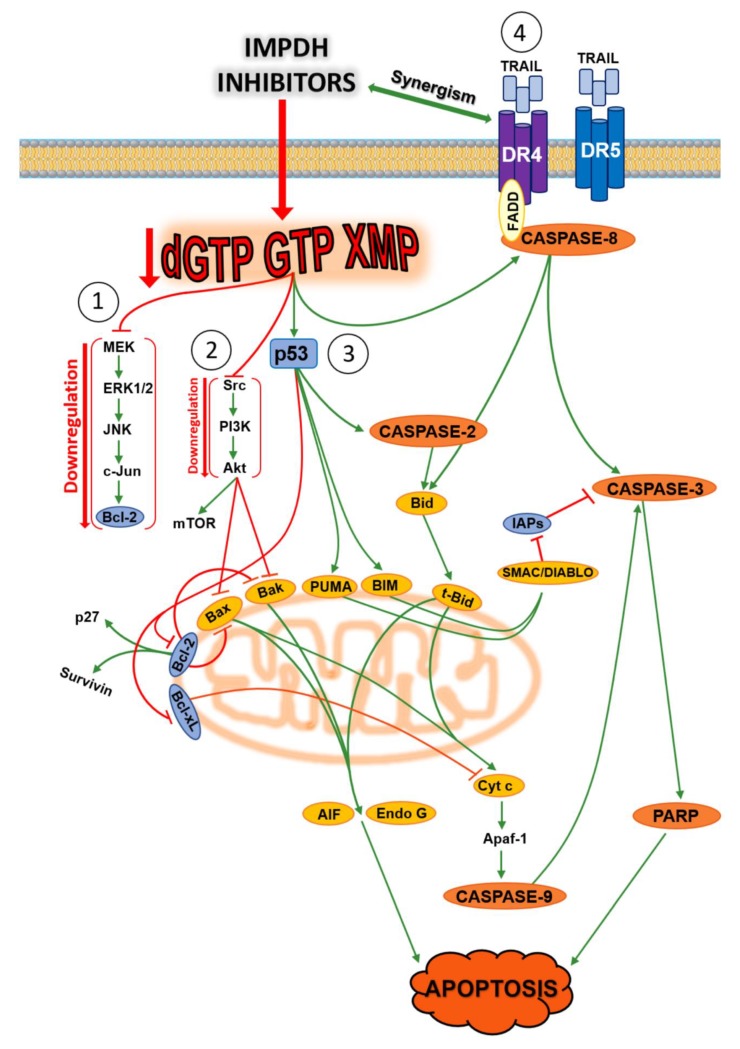
Figure 5.
Apoptotic pathways triggered by inosine 5′-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) inhibitors. The decrease in guanylate pool can trigger apoptosis through multiple pathways: (1): downregulation of the MEK/ERK pathway with inhibition of Bcl-2 and activation of Bax and cytochrome c release [167]; (2): downregulation of Src/PI3K pathway with inhibition of Akt, with downregulation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and activation of pro-apoptotic Bak and Bax with Apoptosis Inducing Factor (AIF) and endonuclease G (Endo G) release from mitochondria (caspase-independent apoptosis) [136,162,163]; (3): upregulation of p53 with (a) downregulation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, with consequent inhibition of p27 and survivin, cytochrome c (Cyt c) release, and activation of caspase-9, caspase-3 and polyADP-ribose polymerase (PARP; intrinsic apoptotic pathway) [159,160,161,164,165], (b) upregulation of PUMA and BIM with consequent SMAC/DIABLO release from mitochondria, inhibition of Inhibitor of Apoptosis (IAPs) (a caspase-3 inhibitor) with activation of caspase-3 [164], and (c) activation of caspase-2 with cleavage of Bid into truncated Bid (t-Bid) and AIF/Endo G release from mitochondria [164]; (4): synergistic effect of IMPDH inhibitors with TRAIL through binding with death receptors (DR4 and DR5) which recruit initiator caspase-8 via the adaptor protein FADD. Activated caspase-8 stimulates apoptosis via two parallel cascades: direct cleavage and activation of caspase-3, or cleavage of Bid into t-Bid which translocates to mitochondria, inducing cytochrome c release, with sequential activation of caspase-9 and -3 (extrinsic apoptotic pathway) [164]. TRAIL: tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; FADD: Fas-associated protein with death domain.