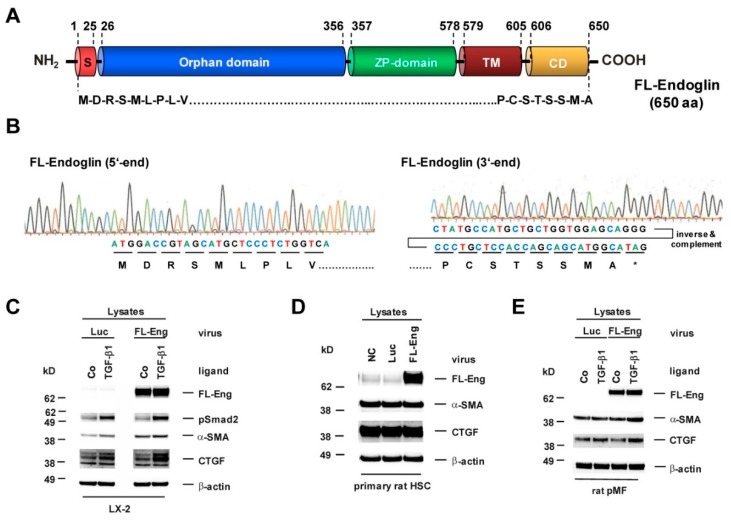
Figure 2.
Structure, sequence analysis and functional expression of a virus coding for full-length Endoglin from rat. (A) The full-length endoglin (FL-Eng) form is composed of a signal peptide, an orphan domain, a zona pellucida (ZP) domain, a transmembrane region (TM), and a cytosolic domain (CD). Amino acid positions spanning individual regions are numbered. (B) Sequence analysis of FL-Eng expression plasmid. For clarity the sequence data of the 3′end was inversed and complemented for depicting the encoded amino acids. (C–E) Human LX-2, primary rat HSC and pMF were infected with a control virus (Luc), FL-Eng or left untreated (NC). Thereafter, cells were treated or not with TGF-β1 (1 ng/mL) for 24 h (C,D), 48 h (E) or cultured without any treatment (Co) (D). Cells were harvested and proteins analyzed using Western blot for transgene expression (FL-Eng), connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) or activation of Smad2 (pSmad2). Equal loading of lanes was proven by re-hybridization of the membranes with an antibody specific for β-actin.