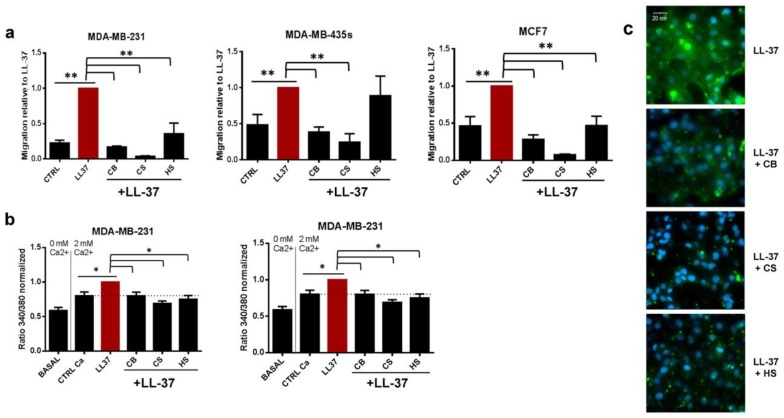
Figure 2.
Glycoaminoglycans (chondroitin sulfate and heparin) inhibit LL-37 induced-calcium entry and migration and reduce its attachment to the cell surface. (a). Migration of MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-435s and MCF7 cell lines induced by LL-37 and incubated or not with different glycoaminoglycans (CB—chondroitin sulfate B at 0.5 mg/mL, CS—chondroitin sulfate from shark cartilage at 0.5 mg/mL, HS—heparin at 50 UI/mL (N = 4)). (b) Calcium entry in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435s induced by LL-37 (10 µg/mL) with or without glycoaminoglycans with concentrations as used for migration (N = 3). (c) Immunofluorescence labeling with anti-LL-37 [22] plus secondary antibody (Alexa488-green) on MDA-MB-231, incubated with or without different glycoaminoglycans with same concentrations as used for migration. Nuclei were labeled by DAPI (in blue). Magnification 400×. Data (migration and calcium entry) are normalized to LL-37. Statistics: ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05, relative to LL-37 and relative to control without LL-37.