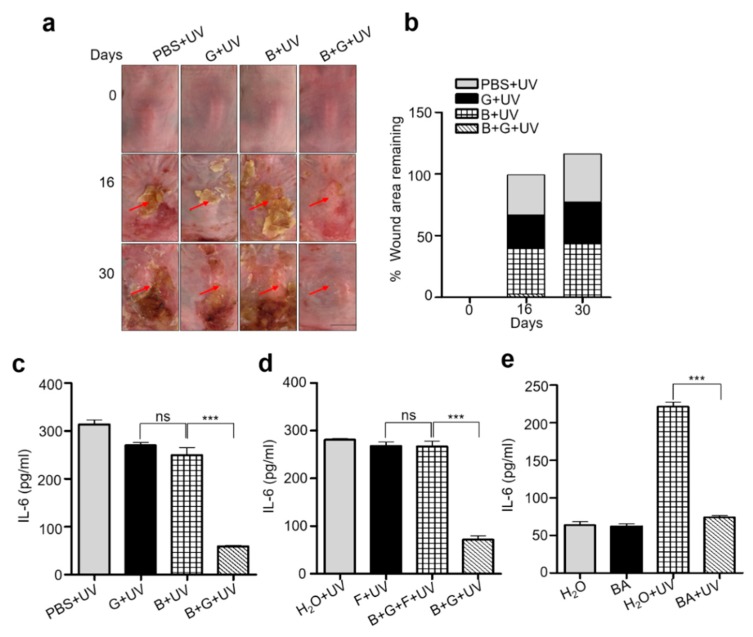
Figure 3.
Attenuation of UVB induced inflammation by application of mixture of S. epidermidis and glycerol and its fermentation metabolite, butyric acid. (a) Skin morphology of ICR mice, topically applied with PBS, glycerol (G) (2%), S. epidermidis bacteria (B) (107 CFU/mL), or mixture of S. epidermidis bacteria plus glycerol (B + G) followed by exposure with UVB (195 mJ/cm2) irradiation are shown at 0, 16, and 30 day. Skin lesions are indicated by red arrows. Scale bar = 5 mm. Graph (b) indicates percent wound area remaining of mice skin. The level of IL-6 in skin (c) from above all groups of ICR mice was quantified using a mouse IL-6 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (R&D Systems). (d) The IL-6 level in skin of ICR mice topically applied with H2O, furfural (0.4%), S. epidermidis bacteria (B) (107 CFU/mL), glycerol (G) (2%) plus furfural (F) (0.4%), (B + G + F) or a mixture of S. epidermidis bacteria plus glycerol (B + G) followed by exposure with UVB (195 mJ/cm2) irradiation is shown. (e) The IL-6 level in skin of ICR mice topically applied with H2O and butyric acid (BA) (4 mM) followed by exposure with UVB (195 mJ/cm2) irradiation is shown. Data are the means of three individual experiments using five mice per group. ns = non-significant. *** p < 0.001. (two-tailed t-tests).