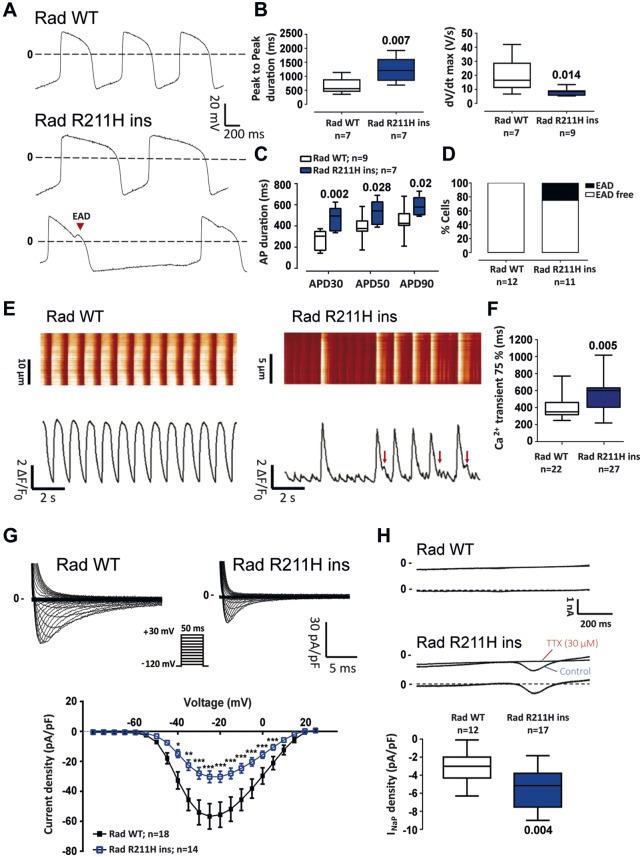
Figure 6.
Rad p.R211H insertion in an extra-familial control line by genome editing: electrophysiological characterization. (A) Representative action potential recordings from control (Rad WT) and mutated (Rad WT) conditions. (B) Box plots of peak to peak duration and action potential upstroke velocity (dV/dt max) of Rad WT and Rad WT cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells Mann–Whitney test. (C) Mean action potential duration (APD) at 30% (APD30), 50% (APD50), and 90% (APD90) of full repolarization at a pacing cycle length of 1 s. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni test for multiple comparisons. (D) Early afterdepolarization incidence in Rad WT and Rad R211H ins cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. (E) Representative [Ca2+]i transients obtained in Rad WT and Rad R211H ins cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells and their corresponding fluorescence map. (F) [Ca2+]i transient 75% decay time (Ca2+ transient 75%) in Rad WT and Rad R211H ins cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells Mann–Whitney test. (G) Superimposed representative INa traces recorded in Rad WT and Rad R211H ins cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (upper panel; voltage-clamp protocol in inset) and mean (±SEM) current density-membrane potential relationships (bottom). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 (two-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni post hoc test for multiple comparisons). (H) Top: representative currents recorded during 1-s voltage-clamp ramps from −120 mV to +40 mV (stimulation frequency: 0.2 Hz) before (Control) and after tetrodotoxin (TTX) perfusion (top traces) in Rad WT and Rad R211H ins cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells and corresponding TTX-sensitive persistent sodium current (INaP, bottom traces). Bottom: box plots of INaP density. Mann–Whitney test.