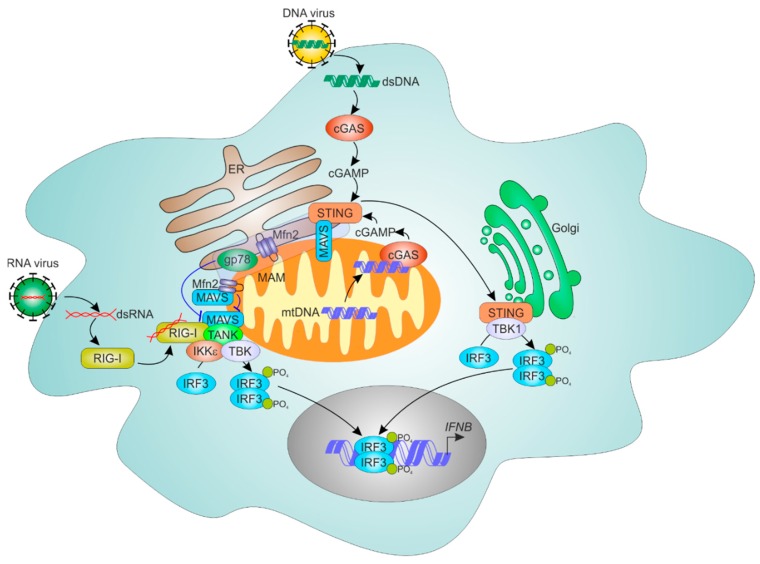
Figure 3.
Communication of ER and mitochondrial in sensing cytosolic nucleic acids. The response to RNA viruses is orchestrated by the sensor retinoic acid inducible gene I (RIG-I), which upon dsRNA recognition translocates to mitochondria- and the MAM-located adaptor MAVS to activate the interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) transcription factor. MAVS may be negatively regulated by their interaction with Mfn2 and Gp78. Sensing of cytosolic DNA involves activation of the cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS)-stimulator of interferon genes (STING) cascade, whereas activated STING translocates from the ER to Golgi to activate IRF3. The cross-talk between DNA and RNA sensing may involve direct interaction of STING and MAVS. cGAS may also sense mtDNA following mitochondrial damage by translocating to mitochondria.