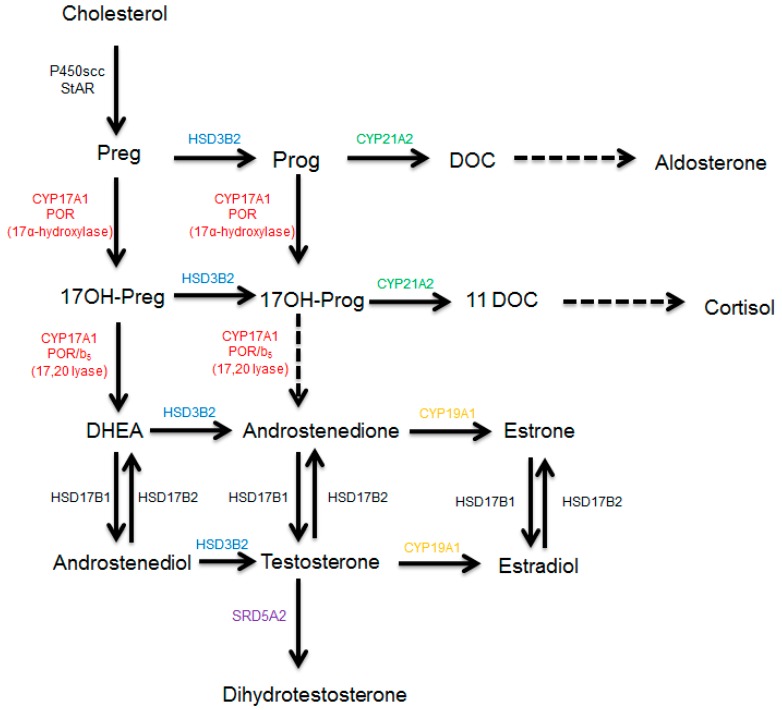
Figure 1.
Synthesis of steroid hormones in humans. After entering the mitochondrion, cholesterol is converted into pregnenolone, which is used as a substrate by CYP17A1 in the endoplasmic reticulum to produce sex steroids. First, the cholesterol is converted into pregnenolone by the enzyme CYP11A1 (P450scc) inside the mitochondria. Pregnenolone is converted into progesterone by HSD3B2 and into 17OH-pregnenolone by the 17α-hydroxylase activity of CYP17A1. Progesterone is converted into deoxycorticosterone by CYP21A2 and into 17OH-progesterone by the 17α-hydroxylase activity of CYP17A1. The 17,20 lyase activity of human CYP17A1 converts 17OH-pregnenolone into DHEA but has poor specificity for 17OH-progesterone as a substrate. The 17OH-progesterone is converted into 11-DOC by the 21-hydroxylase activity of CYP21A2. The CYP19A1 (aromatase) converts androgens into estrogens and uses androstenedione as its major substrate. The 5α-reductase, SRD5A2, converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone. Abbreviations: Preg = pregnenolone, Prog = progesterone, DOC = deoxycorticosterone, 11DOC = 11-deoxycortisol, DHEA = dehydroepiandrosterone, HSD3B2 = 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2, HSD17B1/2 = 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1/2, SRD5A2 = 5α-reductase type 2.