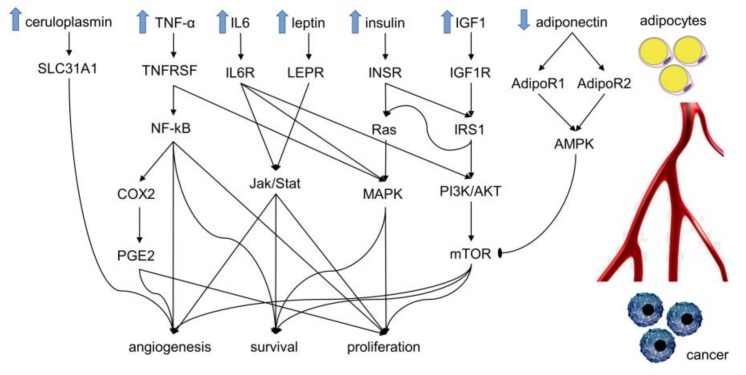
Figure 1.
The pathway shows the influence of adipocytes on cancer. The arrows indicate induction or activation, the line ending with an oval segment (AMPK on mTOR) indicates inhibition. The substances released from adipocytes diffuse through the blood circulation and reach cancer cells where activate different cellular pathways. The latter lead to an increase of cell proliferation, survival and angiogenesis. IGF1: Insulin-like growth factor I. IGF1R: Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. INSR: Insulin receptor. IRS1: Insulin receptor substrate 1. BAD: Bcl2-associated agonist of cell death. MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase. LEPR: Leptin receptor. ADIPOR1: Adiponectin receptor protein 1. ADIPOR2: Adiponectin receptor protein 2. VEGFA: Vascular endothelial growth factor A. AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase. mTOR: Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR. CP: Ceruloplasmin. SLC31A1: High affinity copper uptake protein 1. TNF: Tumor necrosis factor. TNFRSF: Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. IL6: Interleukin-6. IL6R: Interleukin-6 receptor subunit alpha. PTGS2: Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinases. AKT: serine/threonine kinase. HIF1A: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha.