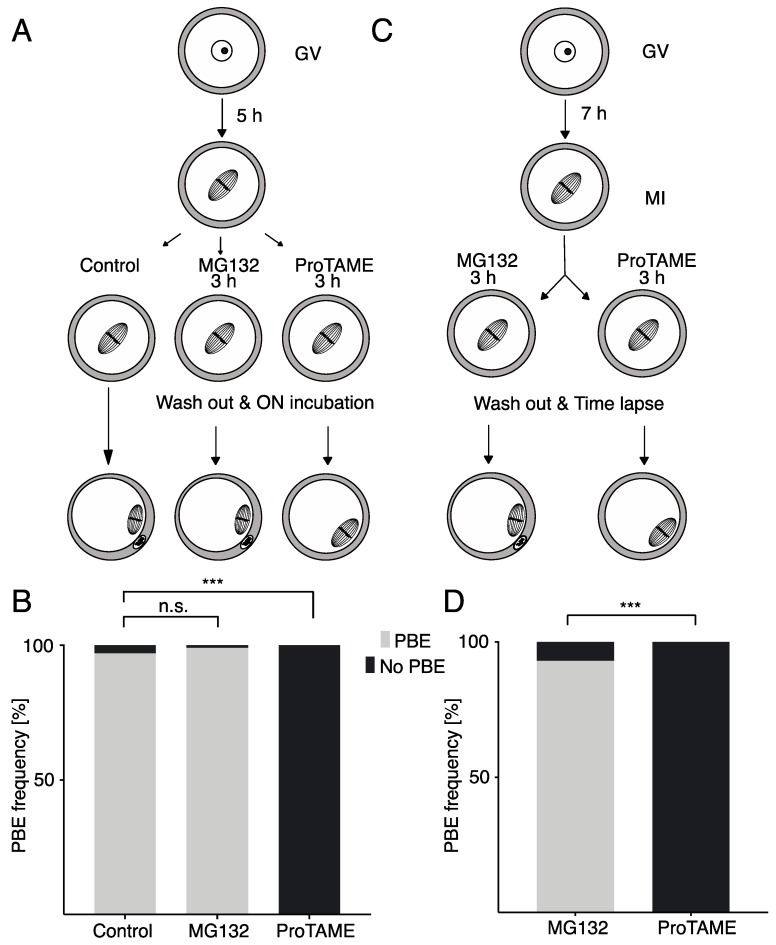
Figure 4.
ProTAME-induced arrest in mouse oocytes is irreversible. (A) Germinal vesicle (GV) oocytes were matured for 5 h and then divided into three groups: the control group, MG132-treated group and proTAME-treated group. The control group was incubated overnight in M16 media. MG132 and proTAME groups were exposed to inhibitors for 3 h, washed out and incubated overnight in M16 media. The frequency of PBE was scored following overnight (ON) incubation. (B) The frequency of PBE in control oocytes (n = 70), oocytes in 10 μM MG132 (n = 79) and oocytes in 5 μM proTAME (n = 81) was scored. A total of 97% of control cells, 99% of cells after MG132 and 0% of cells after proTAME extruded polar bodies (PBs). Data were obtained in three independent experiments. The difference between the control and MG132 is not statistically significant (α < 0.05; p = 0.6008). The difference between the control and proTAME is statistically significant (α < 0.05; *** p < 0.0001). (C) GV oocytes were matured for 7 h and then divided into two groups; one was treated with MG132 and the other with proTAME for 3 h and subsequently cultured in M16 without inhibitors while PBE was monitored by live cell microscopy ON. (D) The frequency of PBE in oocytes after 10 μM MG132 (n = 43) and 5 μM proTAME (n = 51) was scored. A total of 93% of cells after MG132 and 0% of cells after proTAME extruded PBs. Data were obtained in two independent experiments. The difference between both groups is statistically significant (α < 0.05; *** p < 0.0001).