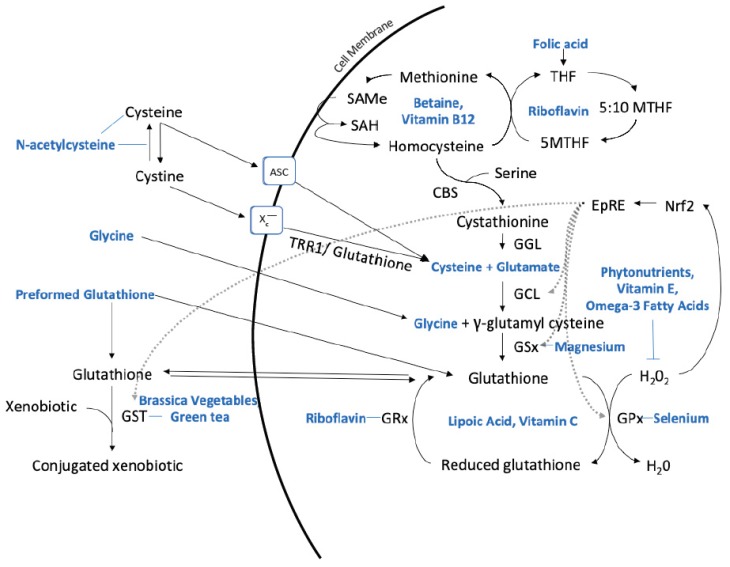
Figure 1.
Hepatic synthesis of glutathione and nutritional substrates, co-factors, and other nutrients that influence metabolism. Key: 5-Methyl-tetrahydrofolate (5MTHF), system alanine–serine–cysteine (ASC), cystathionine-β-synthase (CBS), cystathionine gamma-lyase (CGL), electrophile response element (EpRE), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), glutamate cysteine ligase (GCL), glutathione reductase (GRx), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione synthetase (GSx), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), Nuclear factor erythroid factor-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH), tetrahydrofolate (THF), thioredoxin reductase 1 (TRR1), water (H2O), cystine/glutamate antiporter system (xc−). Description: Folic acid is reduced to THF and converted to 5MTHF which can subsequently be transferred to homocysteine and generate methionine. Methionine forms SAMe, which produces SAH from methylation reactions. SAH is hydrolyzed to homocysteine. Homocysteine can either regenerate methionine or be directed to the trans-sulfuration pathway forming cystathionine via the catalytic activity of CBS and serine. CGL cleaves the sulfur–gamma carbon bond of cystathionine, resulting in the release of cysteine which can be used by GCL and GSx to form glutathione. Extracellular cysteine can be either taken up by the cysteine transporter ASC or oxidized to cystine and taken up by system xc−. N-acetylcysteine can donate cysteine or reduce plasma cystine to cysteine. Intracellular cystine is reduced to cysteine via TRR1 or glutathione. The synthesis of γ-glutamyl cysteine is catalyzed by GCL from cysteine and glutamate, and the addition of glycine to γ-glutamyl cysteine via GSx generates glutathione. GPx catalyzes the reduction of H2O2 by glutathione and forms reduced glutathione which is then recycled to glutathione by GRx. Glutathione can also form adducts and conjugate xenobiotics via GST. Oxidative stress activates the Nrf2 pathway which induces EpRE-dependent gene expression of enzymes involved in glutathione metabolism, including GCL, GSx, GPx, and GST, to re-establish cellular redox homeostasis. Modified and developed from [10,11,12,13,14].