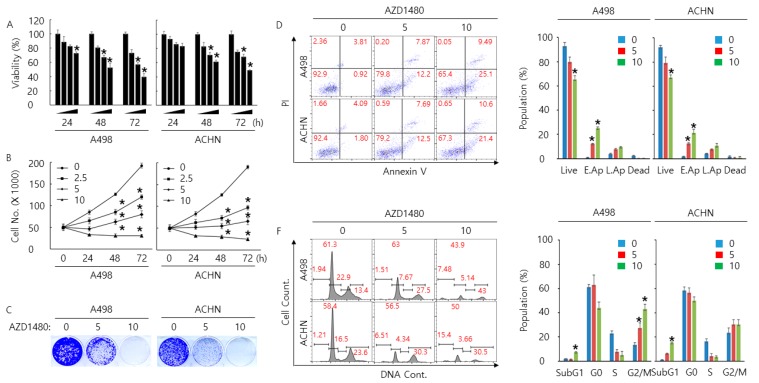
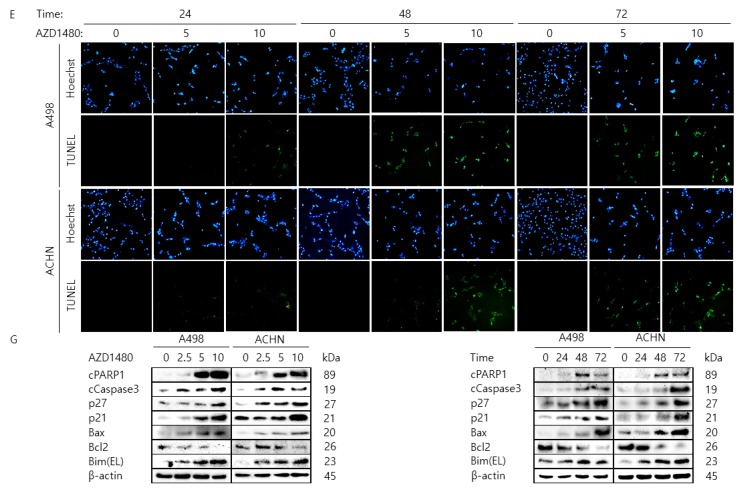
Figure 5.
Anti-cancer effect by AZD1480 treatment in A498 and ACHN cells. (A) Dose and time-dependent anti-cancer effect by the indicated concentration of AZD1480 treatment in A498 and ACHN cells for 24, 48, and 72 h. Cell viability and proliferation rate was determined by WST-1 assay (A) and cell counting assay (B), respectively. This result is representative data from three biological replicates, and the error bar indicates standard error (STE). * indicates the p-value < 0.05. (C) Anti-colony formation ability by the indicated concentration of AZD1480 treatment in A498 and ACHN cells was determined by colony formation assay for 14 days. This result is representative data from three biological replicates. Apoptosis in A498 and ACHN cells treated by the indicated concentration of AZD1480 was determined by Annexin V staining analysis (D) and TUNEL assay (E). Live: live cells, E.Ap: early apoptotic cells, L.Ap: late apoptotic cells, and dead: dead cells. Cell cycle arrest was determined by cell cycle analysis (F). These results are representative data from three biological replicates. (G) Dose and time-dependent western blotting analysis of proteins related to apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in A498 and ACHN cells treated by the indicated concentration of AZD1480. β-actin was used for a gel-loading control. Magnification for (E): ×20.