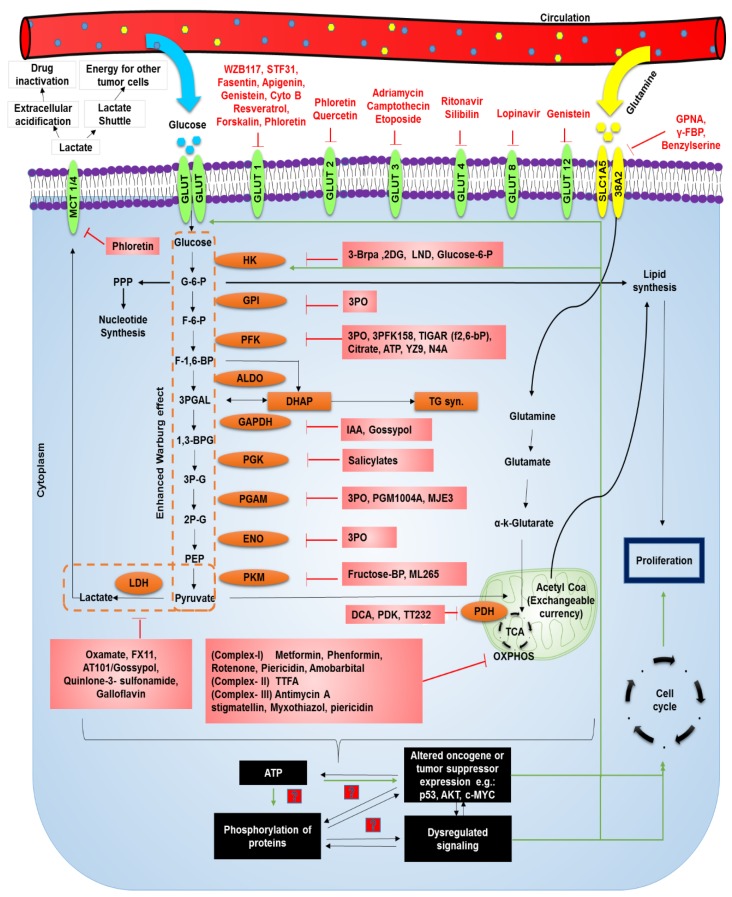
Figure 2.
Hyperglycemia associated metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells and potential targets. Pathways altered due to hyperglycemia leading to proliferation are indicated by green arrows. Inhibitors of various molecules are indicated in red. The inhibitors presented here and the corresponding clinical or research studies are mentioned in Table 1 with their respective targets. STF31: 4-[[[[4-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)phenyl]sulfonyl]amino]methyl]-N-3-pyridinyl-benzamide; CYTO B: Cytochlasin B; GPNA: L-γ-Glutamyl-p-nitroanilide; FBP: Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; GLUT: Glucose transporter; MCT: Monocarboxylate transporter; PPP: Pentose Phosphate Pathway; G6P: Glucose-6-phosphate; F6P: Fructose-6-phosphate; F1,6BP: Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; 3PGAL: Glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate; 13BPG: 1,3 Bisphosphoglyceric acid; 3PG: 3-phosphoglycerate; 2PG:2-phosphoglycerate; PEP: Phosphoenol pyruvate; HK: Hexokinase; GPI: Glucose-6 phosphate isomerase; PFK: Phosphofruktokinase-1; ALDO: Aldohexose; DHAP: Dihydroxyacetone phosphate; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PGK: Phosphoglycerate kinase; PGAM: Phosphoglycerate mutase-1; ENO: Enolase; PKM: Pyruvate kinase M1/M2; TG: Triglyceride; 3BRPA: 3 Bromopyruvic Acid; 2DG: 2-deoxyglucose; LND: Lonidamine; 3PO: (2E)-3-(3-Pyridinyl)-1-(4-pyridinyl)-2-propen-1-one; TIGAR: TP53-inducible glycolysis and apoptosis regulator; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; IAA: 1-O-Indol-3-ylacetyl-beta-D-glucose; DCA: Dichloroacetic acid; PDK: Pyruvate Dehydrogenase kinase; LDH: Lactate Dehydrogenase; OXPHOS: Oxidative phosphorylation.