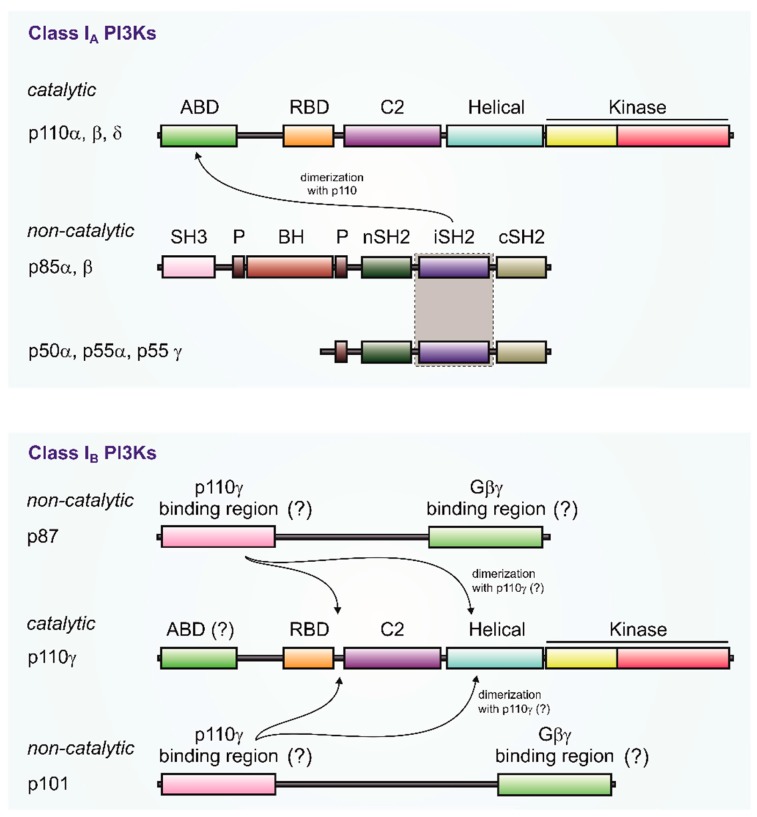
Figure 2.
Modular organization of class I PI3K subunits. Class I PI3Ks are heterodimeric lipid kinases consisting of catalytic and non-catalytic subunits. Class I PI3Ks are further subdivided into class IA and class IB. Catalytic subunits of class IA (p110α, p110β or p110δ) form heterodimeric complexes with any of the p85-related non-catalytic subunits (p50α, p55α, p55γ, p85α, or p85β). Class IA p110 subunits comprise an adaptor-binding domain (ABD), a Ras-binding domain (RBD), a C2 domain, a helical domain, and a kinase domain which is subdivided into N-terminal and C-terminal lobes. All p85-related subunits contain N- and C-terminal Src homology 2 domains (nSH2 and cSH2) separated by a coiled-coiled inter-SH2 domain (iSH2) which is responsible for dimerization with p110 ABD. The p85α and p85β subunits additionally possess Src homology 3 domain (SH3) and a Bar cluster region homology domain (BH) which is flanked by two proline-rich regions (P). Class IB p110γ subunits bind non-catalytic p87 or p101 subunits, forming two distinct heterodimeric enzymes. The modular structure of p110γ is similar with class IA p110 subunits. The presence and the role of the ABD is not fully understood. N- and C-terminal regions of p87 and p101 show a high degree of amino-acid similarity and are involved in direct interaction with p110γ and Gβγ, respectively. HDX-MS comparison of heterodimeric PI3Kγ enzymes proposed a role of the RBD-C2 linker and the helical domain in direct interaction with p87 or p101 [37,54].