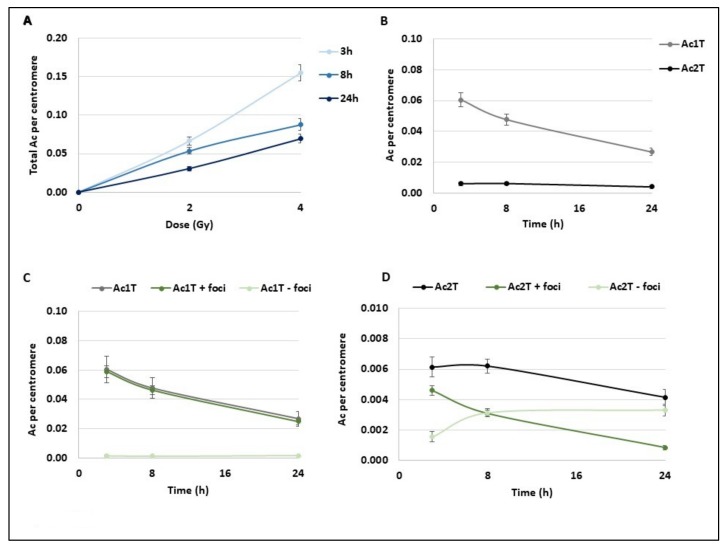
Figure 3.
Kinetics of different subtypes of acentric fragments after radiation exposure. Blood samples from three donors were irradiated at 2 or 4 Gy or kept free from ionising radiation and analysed using the PCC technique. (A) After Telomere/Centromere staining on PCC, the total number of acentric fragments per centromere was scored for each dose and 3 h, 8 h, and 24 h post-IR. The total acentric fragments increase with dose and decrease overtime. Bars represent standard deviation. (B–D) Focus was made on PCC analysis after 2 Gy radiation exposure. Bars represent standard deviation. (B) Acentric fragments containing 1 telomere or resulting from fusion and containing 2 telomeres were separately represented at 3 h, 8 h, and 24 h post IR. A decrease of both types of acentric fragments is observed overtime (C,D) All acentric fragments were counted and classified in two classes, acentric fragments signalled by γ-H2AX foci or without γ-H2AX signal. Their proportions were followed at 3 h, 8 h, and 24 h post IR. Acentric fragments with 1 telomere resulting from one DNA DSB (C) and acentric fragments with 2 telomeres resulting from two DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) and fusions of two fragments (D) were represented separately.