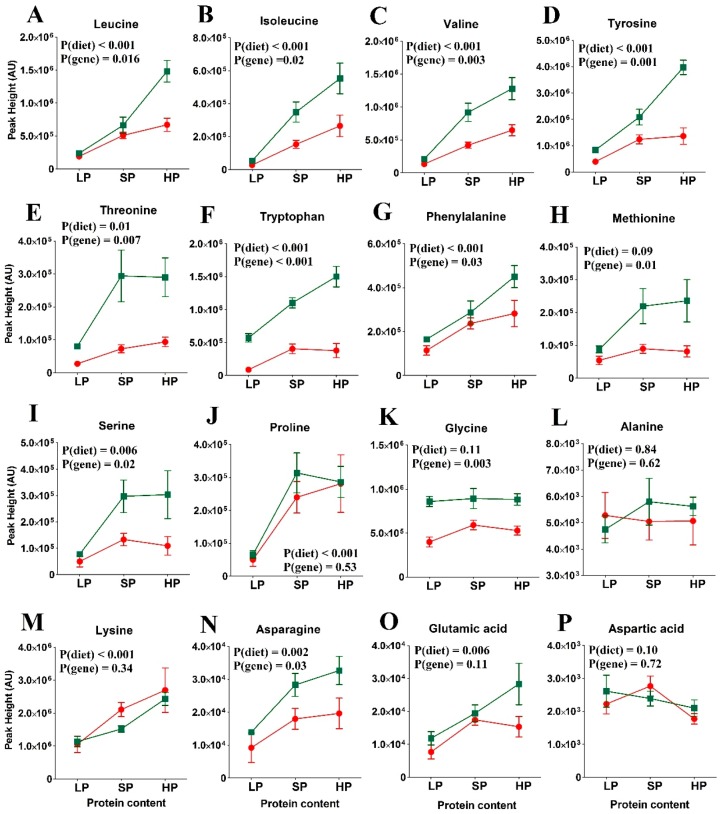
Figure 3.
Postprandial amino acid abundance in SLC6A19ko (red) and wt (green) mice on diets with low (LP), standard (SP), or high protein (HP) contents (n = 5 per group). Amino acids: (A) Leucine, (B), Isoleucine, (C) Valine, (D) Tyrosine, (E) Threonine, (F) Tryptophan, (G) Phenylalanine, (H) Methionine, (I) Serine, (J) Proline, (K) Glycine, (L) Alanine, (M) Lysine, (N) Asparagine, (O) Glutamic acid and (P) Aspartic acid. Levels of all essential amino acids positively correlated with the dietary protein content in the wt mice. SLC6A19ko mice exhibited reduced levels of neutral amino acids due to their dependence on SLC6A19 for amino acid absorption. Note the most prominent difference in plasma amino acid levels between SLC6A19ko and wt was observed following the HP diet. Non-essential amino acids showed no difference between SLC6A19ko and wt mice. The data points represent (n = 5 per group). p-values were calculated by ANOVA comparing within-group and between-group variance of the diet effects (diet) and genotype effects (gene).