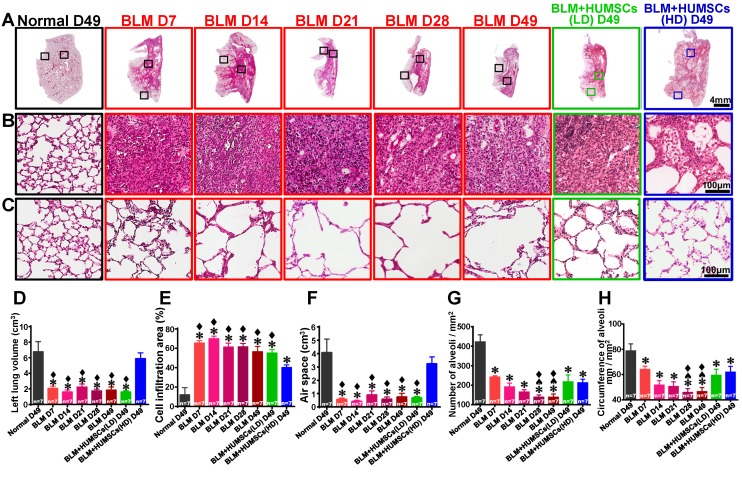
Figure 3.
HUMSC transplantation repaired alveolar structures in PF rats. The left lung tissue slices from each group were stained with H&E (A). (B) and (C) are enlarged images from the central and peripheral regions, respectively. The results revealed a large cell infiltration in the center areas of the left lungs after BLM injection. Transplantation of high doses of HUMSCs ameliorated cell infiltration conditions in the central areas of the left lungs (B). The total left lung volume was quantified by summing data from all left lung sections, demonstrating that the transplantation of high doses of HUMSCs substantially increased the total left lung volume (D), raised the left lung air space (E), and effectively reduced cell infiltration areas in the left lungs (F). With a relatively small morphology, the number of alveoli per unit area was relatively high in the peripheral region of the left lung in the Normal group (C). Following BLM, the morphology of the alveoli became larger, and therefore, the number of alveoli per unit area decreased. In the group transplanted with HUMSCs, the alveoli were relatively small in morphology (C). The quantification of the number (G) and the circumference of the alveoli (H) per unit area in the peripheral regions of the left lung indicated that transplantation of HUMSCs effectively increased the number of alveoli and circumference per unit area for gas exchange. n=7 animals per group. ✱ vs the Normal group, p < 0.05. ♠ vs the BLM+HUMSCs (LD) group, p < 0.05. ⧫ vs the BLM+HUMSCs (HD) group, p < 0.05.