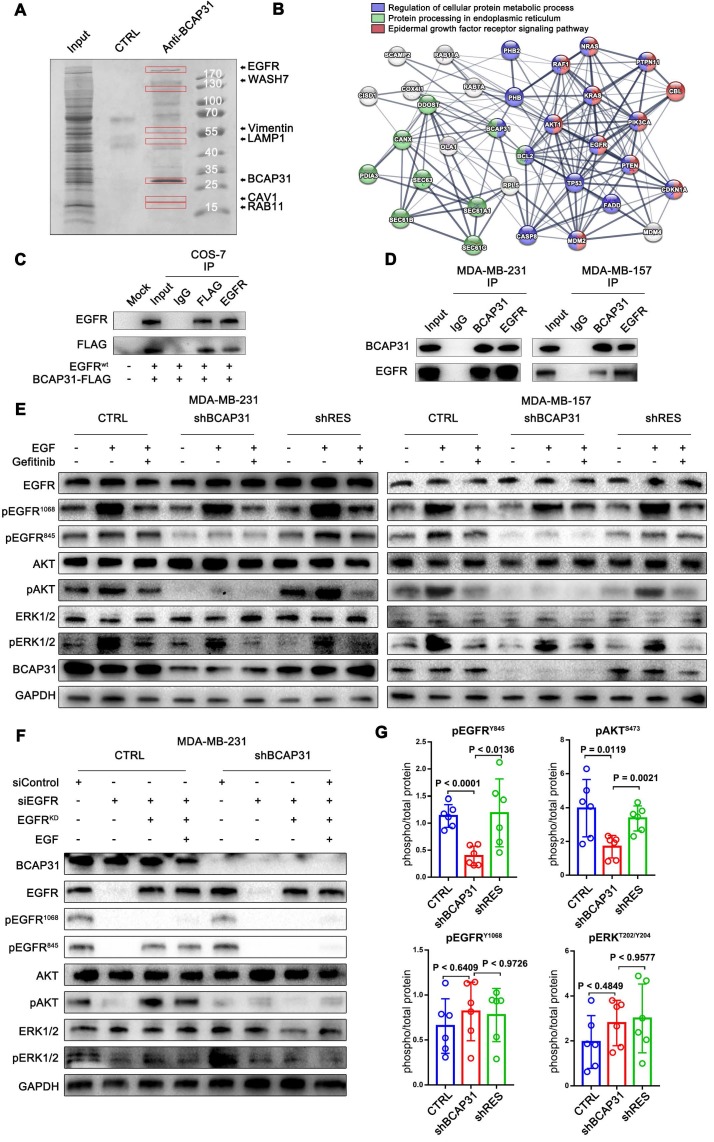
Figure 4.
BCAP31 interacts with EGFR and facilitates ligand-independent EGFR/AKT pathway activation. (A) Mass spectrometry (MS) analysis of BCAP31-associated proteins. The purified protein complex was resolved on SDS-PAGE, followed by silver staining; then, the bands were retrieved and analysed by MS. (B) Analyses of the identified BCAP31 interactors. The diagram depicts BCAP31 interactors as detected by MS. The network was built based on the interaction network of EGFR-associated signalling and trafficking processes in the KEGG database overlaid with MS data. (C and D) The interaction between exogenous and endogenous BCAP31 and EGFR. Co-IP assay and immunoblot analyses evaluating the BCAP31-EGFR interaction in COS-7 cells and TNBC cells. (E) Downregulation of BCAP31 significantly attenuates ligand-independent signalling. TNBC cells stably expressed shBCAP31, control shRNA, or shRES when treated with EGF or EGF combined with gefitinib. IB examinations of phosphorylated EGFR and downstream signalling are shown. (F) Re-expression of the K721A kinase-dead (EGFRKD) EGFR rescues the ligand-independent phosphorylation of EGFR at Tyr 845 and downstream AKT signalling in EGFR-knockdown MDA-MB-231 cells expressing control shRNA but not shBCAP31. SiRNA-resistant EGFR-KD was expressed in control or shBCAP31-MDA-MB-231 cells by lentivirus-mediated infection. Endogenous EGFR was knocked down by siRNA, and whole-cell lysate was harvested for western blot analysis. (G) Tumours of MDA-MB-231 tumour xenografts were harvested, homogenized, and analysed for pEGFR (Tyr1068, Tyr845), pAKT (Ser473), total EGFR and total AKT by ELISA. Statistical significance was determined using Dunnett's test.