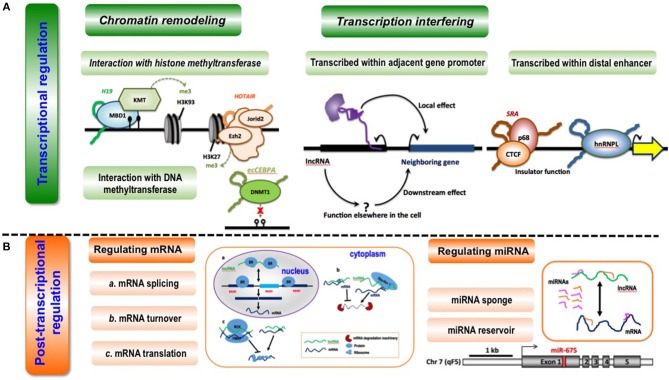
Figure 3.
Conceptual scheme illustrating the primary functionalities of lncRNAs. (A) LncRNA-mediated transcriptional regulation can function through chromatin remodeling (via interaction with histone methyltransferase or DNA methyltransferase) and transcription interfering (via being transcribed within adjacent gene promoters or distal enhancers). Examples are given as below. During interactions with histone methyltransferases, lncRNA H19 binds to the methyl-CpG-binding protein MBD1 to control gene expression by recruiting a histone lysine methyltransferase (KMT) (62); lncRNA HOTAIR interacts with the histone methyltransferase Ezh2, a key component of the PRC2 complex, to mediate chromatin-dependent gene regulation, and also interacts with Jarid2, a PRC2-associated factor, to promote the targeting of PRC2 to chromatin (63). During interactions with DNA methyltransferase, lncRNA ecCEBPA interacts with the DNA methyltransferase DNMT1 to block DNA methylation and control gene expression (64). When being transcribed within adjacent gene promoters, lncRNAs affect the expression of neighboring genes directly via local effect or indirectly via downstream effect (65). When being transcribed within distal enhancers, lncRNA SRA interacts with transcription factor CTCF and its associated DEAD-box RNA helicase p68 to form a complex that is essential for insulator function (66); lncRNA THRIL binds to hnRNPL, a component of hnRNP complexes, and the THRIL-hnRNPL complex regulates transcription by binding to target gene promoters (67). (B) LncRNAs can regulate post-transcription via regulating miRNAs or mRNAs. LncRNAs can modulate mRNA splicing, mRNA turnover and mRNA translation at the post-transcriptional level. LncRNA MALAT1 competes for binding for splicing regulatory proteins SR to assist in pre-mRNA splicing (40); lncRNA Bace1-AS forms a hybrid with Bace1 mRNA to prevent its decay (68), and lncRNAs such as BC058830, AF075069, BC009800 promotes the decay of Alu-containing mRNAs (31); lincRNA-p21 interacts with partially complementary mRNAs of Junb and Ctnnb and suppress their translation via recruiting translation repressors Rck and Fmrp (39), and Uchl1-AS interacts with Uchl1 mRNA via a SINEB2 sequence and a segment fully complementary with the 5′ end of the mRNA to recruit ribosomes and activate Uchl1 mRNA translation (45). LncRNAs can function as a sponge or reservoir of mRNAs during post-transcriptional modulation. LncRNA CCAT1 could function as a molecular sponge of let-7 and to reduce its suppression on the endogenous targets Hmga2 and c-Myc in hepatocellular carcinoma (69); increased lncRNA H19 is associated with decreased Igf1R mRNA expression, as miR-675 that targets Igf1R is embedded in the first exon of H19 (37).