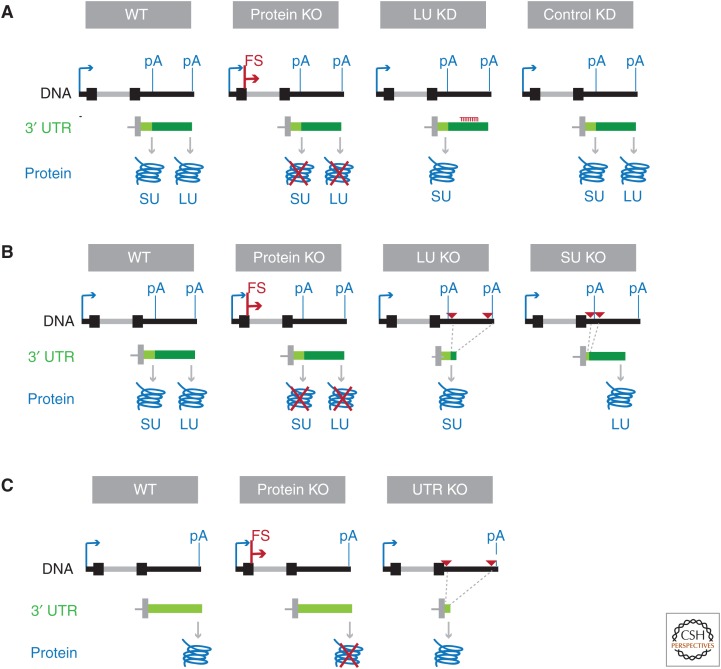
Figure 3.
Experimental approaches using CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) technology at the endogenous locus to study 3′ untranslated region (3′ UTR) functions in vivo. (A) Approach that allows phenotypes obtained for exclusive loss of the LU-generated protein compared with the total protein knockout (KO). Loss of the LU isoform is accomplished through short hairpin RNA (shRNA)-mediated knockdown (KD). At the DNA level, the arrow depicts the transcription start site. pA, Polyadenylation site; FS, frame-shift mutation. In the 3′ UTR panel, the last exon of the messenger RNA (mRNA) isoform is shown with the short 3′ UTR depicted in light green and the long 3′ UTR shown in dark green. The generated proteins are shown in blue. SU, Protein generated from the short 3′ UTR isoform; LU, protein generated from the long 3′ UTR isoform. (B) Approach that allows phenotypes obtained from the total protein KO to be compared to with exclusive expression of the protein generated from either the short (SU) or long 3′ UTR (LU) isoform. Shown as in A. The red triangles represent paired guide RNAs to delete 3′ UTR fragments. (C) Approach that allows the comparison of phenotypes obtained from the total protein KO to those generated by exclusive loss of regulatory elements in the 3′ UTR of genes that generate mRNAs with constitutive 3′ UTRs. Shown as in B. The regulation of mRNA abundance through the endogenous polyadenylation signal is preserved.