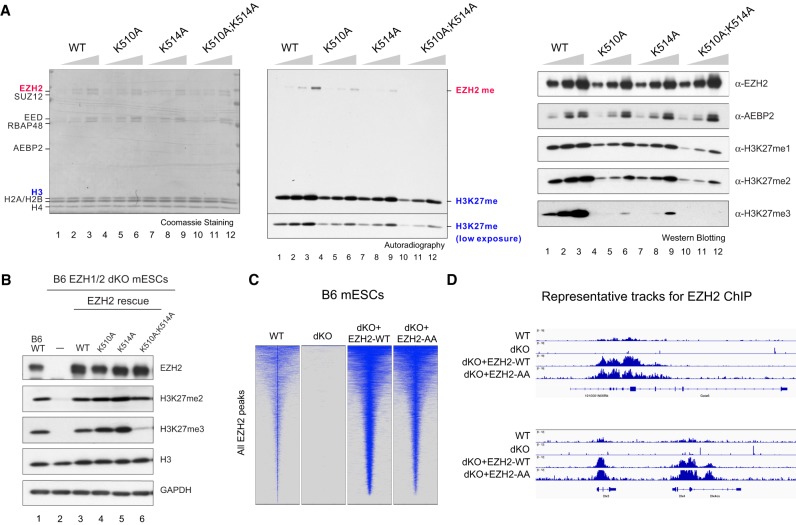
Figure 3.
Residues automethylated in EZH2 are critical for PRC2 catalytic activity. (A) Methyltransferase assays using PRC2–EZH2–AEBP2 complexes containing either 15, 30, or 60 nM wild-type or mutant EZH2 as indicated and 300 nM oligonucleosomes as substrates. (Left) Coomassie blue staining of SDS–polyacrylamide gels containing nucleosomes or PRC2 components was used to visualize the relative concentration of each component present in each reaction. (Middle) Levels of EZH2 or histone H3 methylation are shown by autoradiography. (Right) Western blot analysis of the methyltransferase reaction components (EZH2 and AEBP2) and products (H3K27me1, H3K27me2, and H3K27me3). (B) Western blot analysis of EZH2, H3K27me2, H3K27me3, GAPDH, and total histone H3 levels in B6 mESCs, including WT, EZH1-KO/EZH2ΔSET (dKO), and EZH2 rescue conditions. (mESCs) Mouse embryonic stem cells. (C,D) EZH2 automethylation is not required for PRC2 deposition. (C) Heat maps representing EZH2 ChIP-seq peaks centered by maximum peak intensity at the genome-wide scale in ±10-kb windows within a 200-bp bin size. The genotypes of B6 mESCs for each experimental condition are indicated above. (dKO) EZH1-KO/EZH2ΔSET. (D) Representative track images for EZH2 (blue) ChIP-seq experiments performed in C for a select group of annotated genes. The UCSC annotations of exons and gene bodies are shown at the bottom. The scale of the peaks ranges from 0 to 18 reads per 10 million reads, with spike-in normalization using Drosophila chromatin and Drosophila H2A.X antibody in each ChIP reaction.