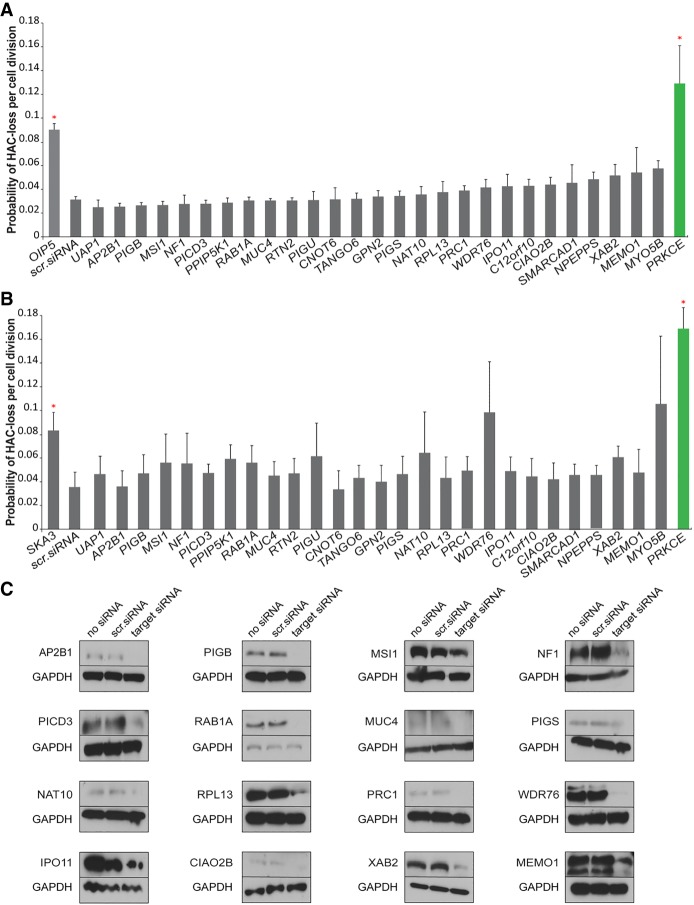
Figure 3.
Mitotic stability of the HAC/dGFP in human HT1080 cells treated with a set of siRNAs against 28 human orthologs of yeast CIN genes. A list of gene orthologs selected for the analysis includes CNOT6, NAT10, PIGB, TANGO6, PIGU, PIGs, GPN2, PRC1, IPO11, CIAO2B, NPEPPS, RTN2, UAP1, MSI1, AP2B1, PPIP5K1, WDR76, C12orf10, PLCD3, MUC4, NF1, RAB1A, MEMO1, SMARCAD1, RPL13, XAB2, MYO5B, and PRKCE genes. Mitotic stability of HAC/dGFP after knockdown of a target gene was measured by flow cytometry (FACS) (A) and HTI (B). Among 28 genes analyzed, the strongest effect on HAC/dGFP stability was revealed after cell treatment by siRNA against PRKCE (green color and red asterisk). siRNAs against OIP5 and SKA3 were used as positive controls for FACS and HTI experiments, correspondingly, and scrambled siRNA (nontargeting siRNA) was used as a negative control. Red asterisks indicate statistical significance (P < 0.05; t-test) when compared to a negative control. (C) Western blot analysis monitoring silencing efficiency of NAT10, PIGB, PIGS, PRC1, IPO11, CIAO2B, MSI1, AP2B1, WDR76, PICD3, MUC4, NF1, RAB1A, MEMO1, RPL13, XAB2, and PRKCE proteins (Supplemental Table S8) after siRNA-mediated knockdown.