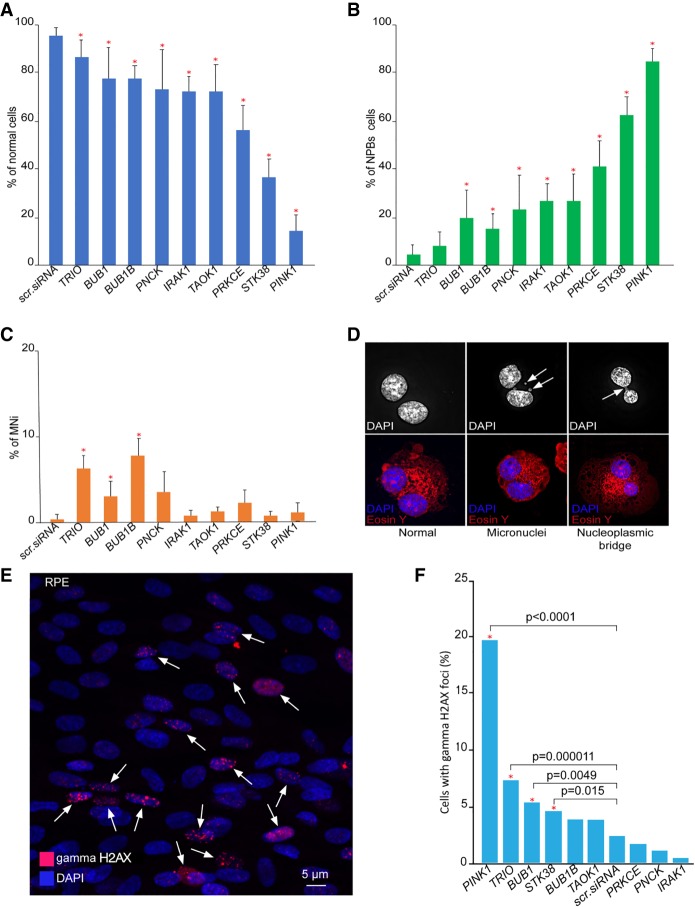
Figure 6.
(A–D) Micronuclei (MNi) and nucleoplasmic bridges (NPBs) formation in RPE cells after knockdown of one of the following genes: TRIO, BUB1, BUB1B, PNCK, IRAK1, TAOK1, PRKCE, STK38, and PINK1. (A) The percentage of the binucleated cells without abnormalities. (B) The percentage of NPBs. (C) The percentage of MNi. Scrambled siRNA (nontargeting siRNA) was used as a negative control. Error bars correspond to a SD of four replicates. Red asterisks indicate statistical significance when compared to the control (calculated by Fisher's exact test with Bonferroni correction for multiple testing, P < 0.0011). (D) A normal binucleated cell; a binucleated cell containing three MNi; a cell containing one NPB. White arrows point to MNi and NPBs. The cells were stained with DAPI and Eosin Y. (E,F) Immunostaining of double-stranded breaks (DSBs) with an antibody against gamma H2AX in interphase of RPE cells after knockdown of PINK1, TRIO, BUB1, STK38, BUB1B, TAOK1, PRKCE, PNCK, and IRAK1 genes. (E) Examples of immunostaining of the cells. Red signals show gamma H2AX staining as a marker for DSBs. Accumulation of gamma H2AX foci occurred at day 3 in all cases. White arrows point to the cell nuclei with gamma H2AX signals. (F) A statistical effect of gamma H2AX foci after knockdown of a target gene. A statistical effect was determined at day 3. For PINK1, TRIO, BUB1, and STK38 genes, statistically significant (Fisher's exact test: P-value; two-tailed) results when compared to a negative control (scr. siRNA or nontargeting siRNA) are indicated with square brackets and red asterisks.