Table 1.
Optimization of the reaction conditions.[a]
| Entry | Catalyst | R | t [min][b] | Yield [%][c] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1[d,e] | FeCl2⋅4 H2O | n‐propyl (2 a) | 20 | 76 (3 aa) |
| 2[d–f] | FeCl2⋅4 H2O | n‐propyl (2 a) | 20 | 5 (3 aa) |
| 3[d] | FeCl2⋅4 H2O | n‐propyl (2 a) | 20 | 84 (3 aa) |
| 4[d] | FeF3 | n‐propyl (2 a) | 20 | 45 (3 aa) |
| 5[d] | FeCl3 | n‐propyl (2 a) | 20 | 73 (3 aa) |
| 6[d] | Fe(acac)3 | n‐propyl (2 a) | 20 | 89 (3 aa) |
| 7 | Fe(acac)3 | n‐propyl (2 a) | 15 | 98 (3 aa) |
| 8 | – | n‐propyl (2 a) | 15 | 0 (3 aa) |
| 9[g] | Fe(acac)3 | n‐propyl (2 a) | 15 | 0 (3 aa) |
| 10[f] | Fe(acac)3 | n‐propyl (2 a) | 15 | 11 (3 aa) |
| 11 | Fe(acac)3 | cyclohexyl (2 b) | 5 | 96 (3 ab) |
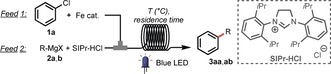
[a] Reaction conditions: Feed 1: chlorobenzene (1 a; 2 mmol), Fe(acac)3 (0.04 mmol), THF (5 mL); feed 2: Grignard reagent (3 mmol), SIPr⋅HCl (0.08 mmol), THF, 25 °C, 24 W blue LEDs. [b] Residence time. [c] The yield was determined by GC. [d] Fe(acac)3 (0.02 mmol), SIPr⋅HCl (0.04 mmol), [e] T=20 °C. [f] No light. [g] No ligand.
