Figure 2.
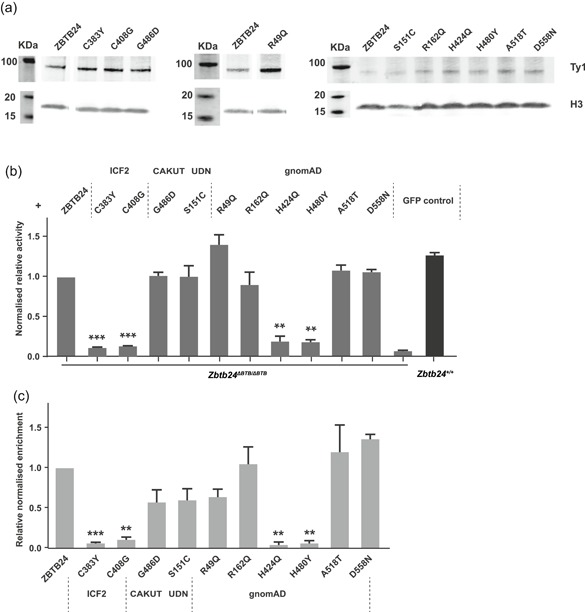
Effects of ZBTB24 variants on ZBTB24 function. (a) Western blot showing the expression levels of Ty1‐tagged wild‐type ZBTB24 and ZBTB24 with different variants in U2OS cells. H3 is used as a loading control. (b) Luciferase reporter assay showing the relative activity of Cdca7 promoter (firefly luciferase normalized to renilla luciferase) regulated by wild‐type mouse Zbtb24 and overexpressed human ZBTB24 or with different variants in homozygous Zbtb24 mutant mESCs. Wild‐type and homozygous Zbtb24 mutant mESCs transfected with GFP were used as positive and negative control. Error bars = SEM from two biological replicates. t test ** p < .01, *** p < .001. (c) ChIP‐qPCR result shows the binding capacities of ZBTB24 or its different variants at CDCA7 promoter region. Error bars = SEM from two independent experiments. t test ** p < .01, *** p < .001. CAKUT, congenital anomalies of the kidneys and urinary tract; ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; gnomAD, Genome Aggregation Database; ICF, immunodeficiency, centromeric instability, facial anomalies; qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction; SEM, standard error of the mean
