Figure 2.
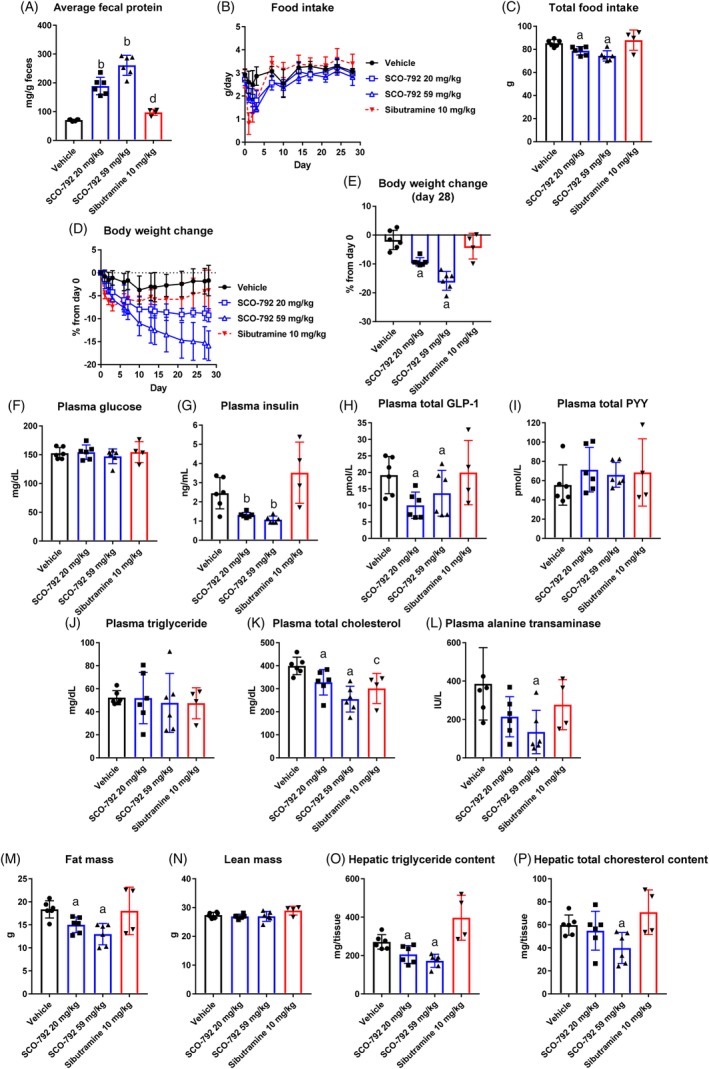
Effects of repeated administration of SCO‐792 on body weight and metabolic parameters in DIO mice. Average fecal protein; A, feces collected at four independent periods: Days 2‐3, Days 6‐7, Days 13‐14 and Days 27‐28. B, food intake during the study. C, total food intake. D, body weight change during the study. E, body weight change at Day 28. At end of study, levels of F, plasma glucose. G, insulin. H, total GLP‐1. I, total PYY. J, triglyceride. K, total cholesterol. L, alanine transaminase. M, fat mass. N, lean mass. O, hepatic triglyceride content and P, hepatic total cholesterol content. SCO‐792 increased fecal protein, a biomarker, inhibited food intake and continued to reduce body weight. Plasma insulin, cholesterol and alanine transaminase levels decreased, along with reductions in fat mass and hepatic lipid content. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 4‐5). a P ≤ .025 vs vehicle by one‐tailed Williams' test. b P ≤ .025 vs vehicle by one‐tailed Shirley‐Williams test. c P ≤ .05 vs vehicle by Student's t‐test. d P ≤ .05 vs vehicle by Aspin‐Welch test
