Figure 1.
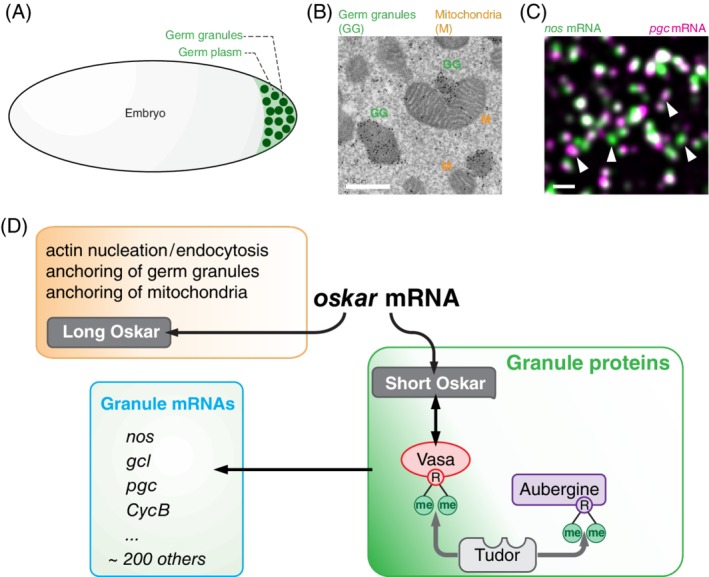
Formation of germ granules in Drosophila embryo (figure adapted from Reference 4. A, Germ granules form in the specialized cytoplasm called germ plasm at the embryo's posterior pole. B, An EM image showing that germ granules (labeled by immunogold particles staining Vasa protein; marked with green “GG”) are more electron dense than surrounding germ plasm and are closely associated with mitochondria (marked with orange “M”). C, Germ granules accumulate nos (green) and pgc (magenta) homotypic mRNA clusters,5, 6, 7 that are often colocalized within the same granule but that do not mix with each other.7 White arrows point at granules that are populated by only nos or pgc demonstrating that germ granules are heterogeneous in mRNA composition. D, oskar mRNA translates into Long and Short Osk isoforms that regulate distinct aspects of germ plasm and germ granules formation. R‐me indicates a methylated arginine. Scale bar in B is 500 nm and in C it is 1000 nm
