Figure 5.
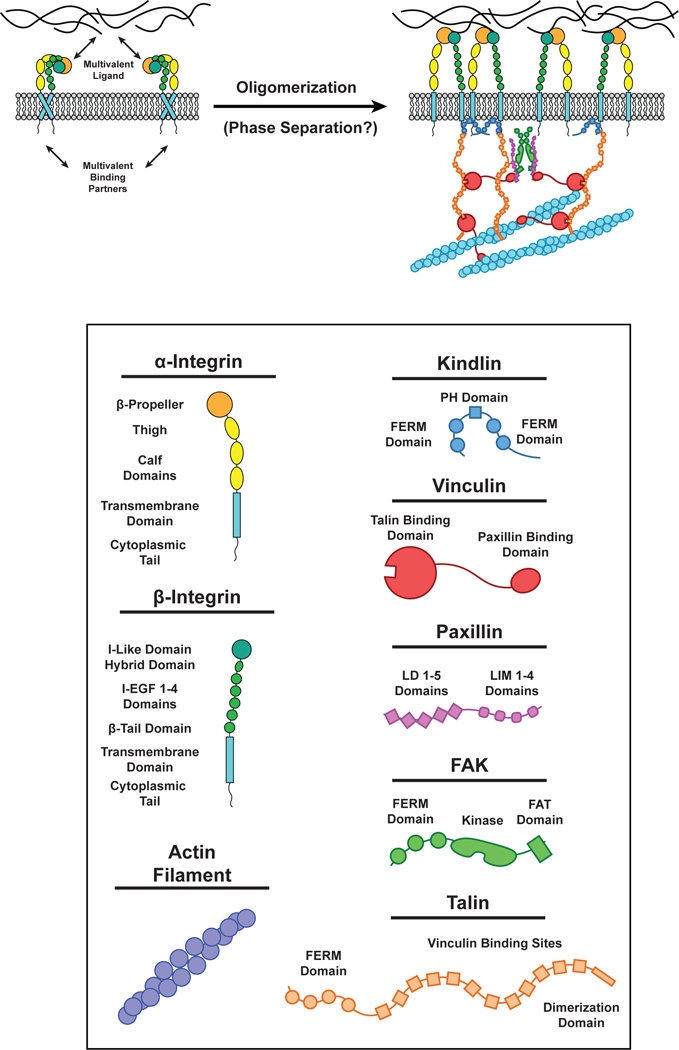
Multivalent interactions at Focal Adhesions. (LEFT) Integrin receptors in the inactive conformation. (RIGHT) Integrin receptors can be activated when the extracellular domain binds multivalent components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and the intraceullar domain of β-integrin binds Kindlin (Blue) and/or Talin (Orange). Kindlin dimerizes by interactions in the FERM domain. Talin is composed of ten Vinculin (Red) binding sites and can bind actin filaments by a site in its C-terminus dimerization domain. Vinculin can bind Talin (via its N-terminal Talin binding domain) and Paxillin (Purple) LD motifs and actin filaments by a site on its C-terminus. Paxillin LD motifs can bind the Vinculin C-terminus and FAK FAT domains. FAK (Green) can dimerize by interactions between its FERM domains. Each of these unique interactions between multiple proteins results in the formation of a highly interconnected oligomeric protein network in focal adhesions.
