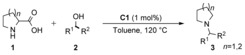
Table 3.
Decarboxylative N‐alkylation of amino acids with secondary and long‐chain alcohols.[a]
| Entry | Product | Yield[b] [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|
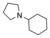
| 1 | 3 aq |
|
57 |
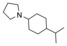
| 2 | 3 ar |
|
76[c] |
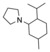
| 3 | 3 as |
|
0 |
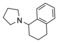
| 4 | 3 at |
|
49 |
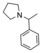
| 5 | 3 au |
|
62 |
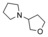
| 6 | 3 av |
|
42[c] |
| 7 | 3 aw |
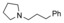
|
81[d] |
| 8 | 3 ax |
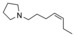
|
51[c] |
| 9 | 3 ay |
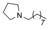
|
54 |
| 10 | 3 by |
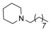
|
55 |
[a] General reaction conditions: 0.5 mmol of 1, 1 mmol of 2, 1 mol % C1, 2 mL toluene, 24 h, 120 °C, under argon. [b] Isolated yields. [c] Yields are based on 1H NMR spectroscopy, using 1,3,5‐trimethoxybenzene as an internal standard. [d] Reduced double bond in the product (note: 2 equiv. of alcohol used).
