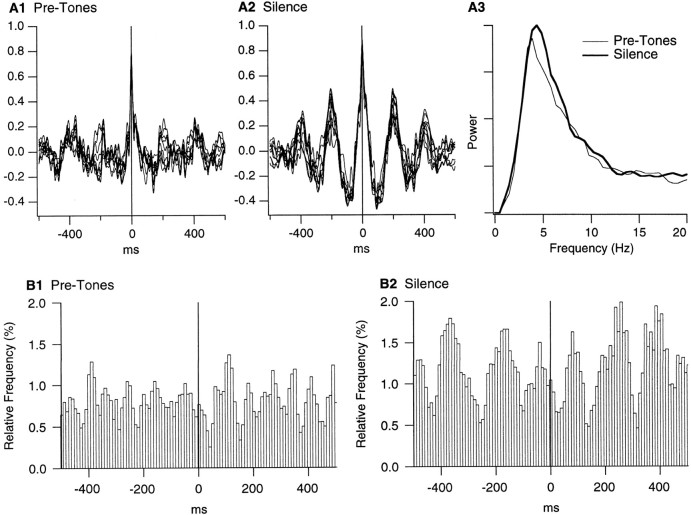
Fig. 7.
Simultaneously recorded LA sites exhibit increased correlation in the theta band during the anticipation of noxious stimuli. A, Cross-correlograms of local field potentials recorded simultaneously in two LA sites (distance, 0.8 mm) before the tones (A1) and during the silent period (A2). Focal waves were digitally filtered from 2 to 55 Hz and divided in 1 sec segments sliding in steps of 100 msec over the 5 sec epoch preceding the tones or the silent period. Then, the corresponding wave segments were cross-correlated. Only 10 of the resulting cross-correlograms are shown in A1 andA2. A3, Power spectrum of cross-correlograms before the tones (thin line) and during the silent period (thick line). To compute this, the analysis described in A1 and A2 was repeated for all pairs of simultaneously recorded LA sites (n = 59), and the FFTs of the resulting cross-correlograms were averaged. B, Population perievent histograms of LA firing using the positive peaks of focal theta waves as reference times, before the tones (B1) or during the silent period (B2). Average of 49 perievent histograms. To compute these histograms, focal waves were digitally filtered (4–7 Hz), and the positive peaks of theta waves exceeding 1.5 times the SD of the 5 sec segments were detected. The number of theta peaks and spikes were 803 and 652 for B1 compared to 1076 and 1986 for B2.