Fig. 9.
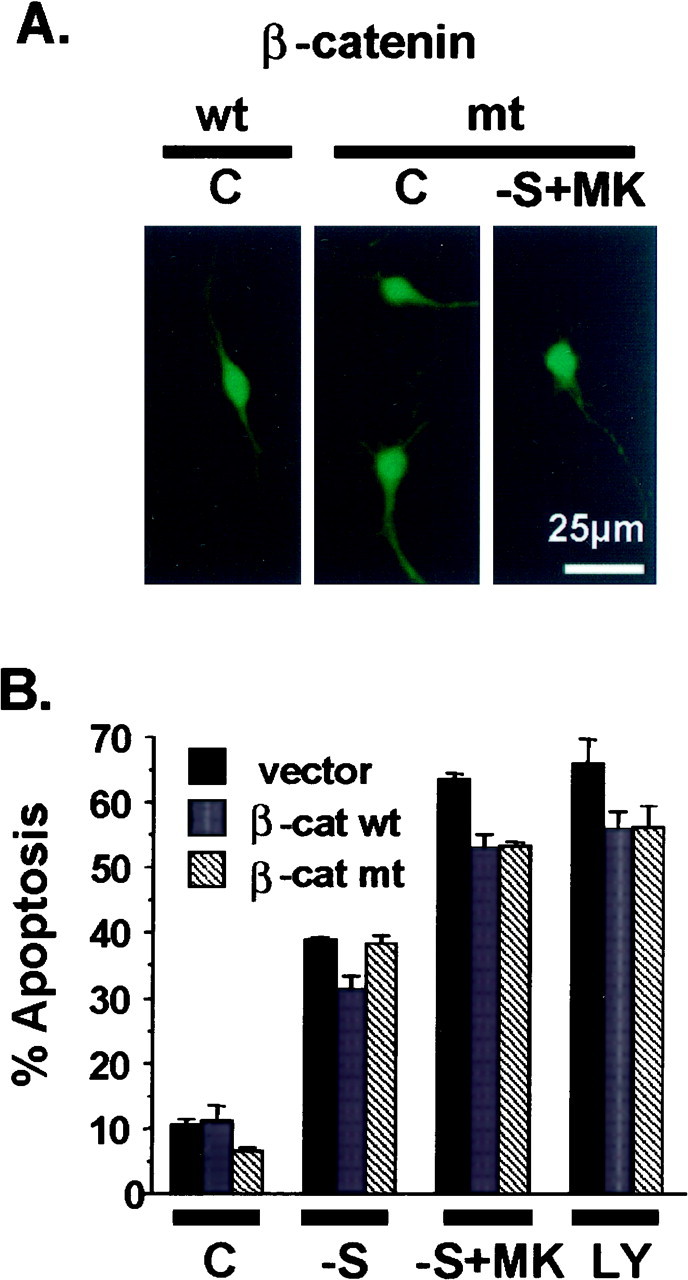
Expression of β-catenin does not protect cortical neurons from apoptosis induced by trophic withdrawal. Cortical neurons were transfected with 4 μg of plasmid DNA encoding the wild-type (β-cat wt) or a mutant form (β-cat mt) of β-catenin. The cloning vector was used as a control (vector). All four of the serine residues in β-catenin, which are targeted by GSK3β, were mutated to alanines in the mutant form of β-catenin, which is stable and not subject to GSK3β-induced degradation. Cells were also cotransfected with an expression vector encoding β-galactosidase (2 μg) as a marker for transfection. Two days after transfection, neurons were either fixed directly (C) or treated with serum deprivation (−S), serum deprivation with 10 μm MK-801 (−S+MK), or 30 μmLY294002 (LY) for 24 hr. A, Representative photomicrographs depicting immunostaining with 9E10 antibody to detect transfected Myc-tagged β-catenin.B, Apoptosis in the transfected cell population (β-galactosidase-stained cells) was quantitated. Data are averages of duplicate determinations. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments. At least 350 transfected cells were scored for each condition. Error bars are SEM.
