Fig. 10.
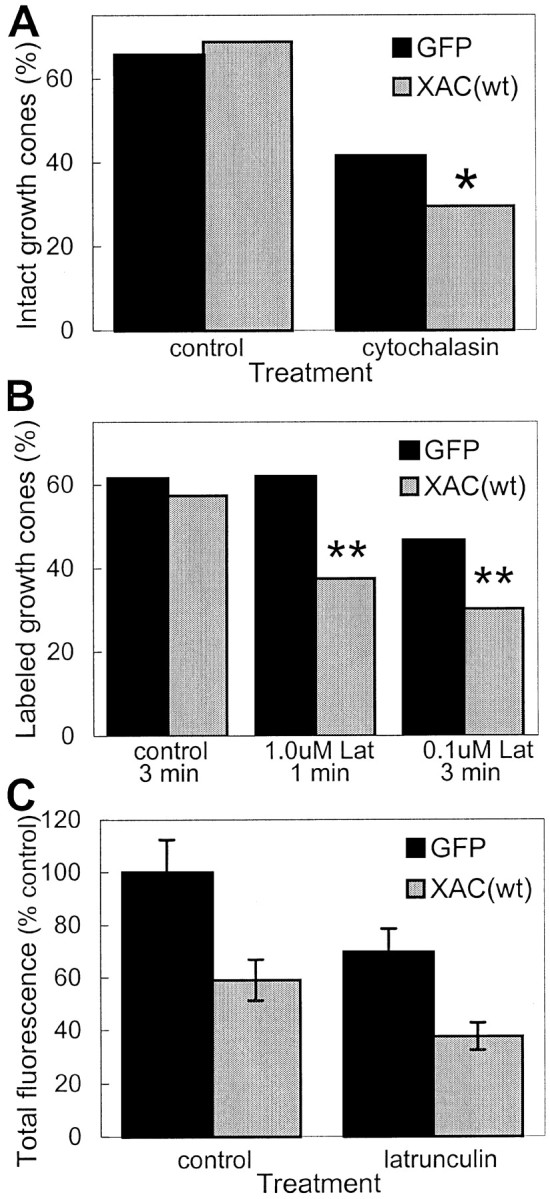
Decreased stability of actin filaments in growth cones of XAC(wt)-expressing neurons. A, Treatment of rat cortical neurons with 1.0 μm cytochalasin D for 45 sec caused a greater loss of intact growth cones in neurons infected with adXAC(wt) than those infected with adGFP (*p < 0.05; χ2 test). The percentage of intact growth cones was similar in vehicle-treated control cultures not exposed to cytochalasin D. Growth cones were considered intact if the neurite tip was wider than the neurite shaft and phalloidin fluorescence was at least three times the intensity found in the neurite shaft. The longest neurite on each neuron was assayed. B, Neurons expressing XAC(wt) were more susceptible to losing identifiable, phalloidin-labeled growth cones than GFP-expressing controls after LatA exposure. Cells were exposed to LatA or control medium and then Triton-extracted in the presence of phalloidin (see Materials and Methods). Treatment of GFP-expressing neurons with 1.0 μmLat A for 1 min had almost no effect on the percentage of labeled growth cones but decreased labeled growth cones by more than a third in XAC(wt)-expressing neurons (**p < 0.01; χ2 test). Treatment with LatA for a longer duration (3 min), even at lower concentration (0.1 μm), caused a greater decline in phalloidin labeling, with the effect again being more pronounced on XAC(wt)-expressing neurons when compared with GFP-expressing ones (**p < 0.01; χ2test). C, Relative fluorescence in growth cones after the Triton-extraction procedure is shown. Averages are expressed relative to total fluorescence in adGFP-infected cultures not exposed to LatA. Because phalloidin fluorescence of growth cones could only be detected in a fraction of XAC(wt)-expressing neurons, only a similar fraction of growth cones from GFP-expressing neurons were selected, corresponding to the most highly labeled growth cones (if 100 XAC(wt)-infected neurons were analyzed and only 30 had identifiable phalloidin-labeled growth cones, then only the brightest-labeled 30 growth cones were selected for comparison from the GFP-infected neurons).
