Fig. 1.
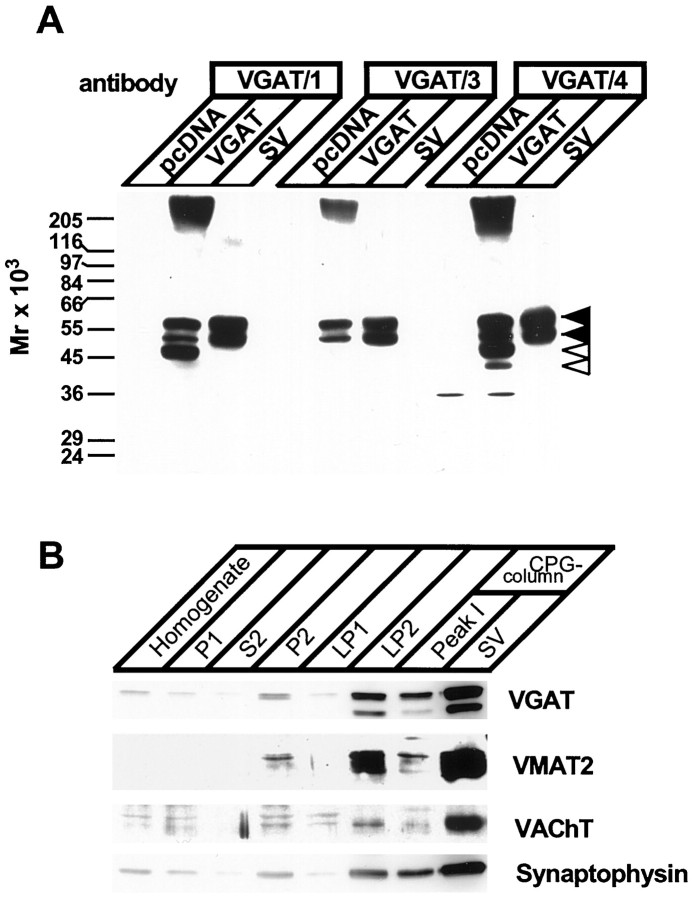
Characterization of antibodies specific for the VGAT. A, Antibodies specific for the N- (VGAT/1 and VGAT/3) or C-terminal (VGAT/4) domain recognize identical bands in synaptic vesicles and in cells expressing VGAT. tsA201 cells were transiently transfected with either a rVGAT plasmid (VGAT) or a plasmid without insert (pcDNA) and analyzed by immunoblotting. For comparison, purified synaptic vesicles (SV) were analyzed in parallel. All three antibodies recognized a doublet band (57 and 50 kDa) in both synaptic vesicles and transfected cells (filled arrowheads). Note that some degradation was observed in the heterologous expression system (open arrowheads). B, VGAT copurifies with other vesicular transporters and the vesicle protein synaptophysin during the isolation of synaptic vesicles. Synaptic vesicles were purified using established procedures, with the following fractions being analyzed:Homogenate; P1, crude nuclear pellet;P2, crude synaptosomes (10,000 × gpellet); S2, 10,000 × gsupernatant; LP1, 25,000 × g pellet obtained after synaptosomal lysis; LP2, crude synaptic vesicles; Peak 1 and SV, large membrane and purified synaptic vesicles as separated by controlled-pore glass (CPG) bead chromatography, respectively (for details, see Huttner et al., 1983; Hell and Jahn, 1994).