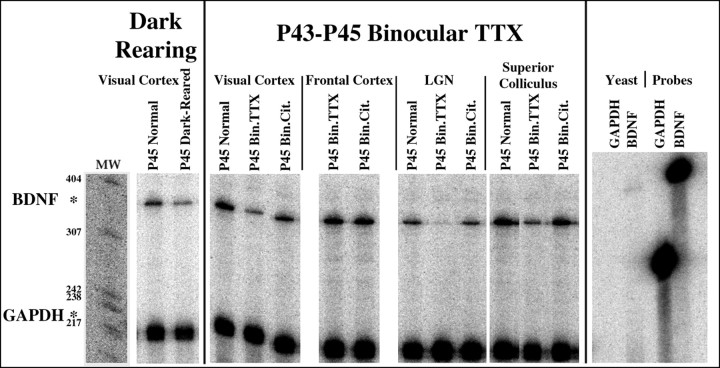
Fig. 1.
RNase protection assessment of dark-rearing or brief binocular TTX injections on BDNF mRNA levels in visual structures of the cat during the critical period. Animals used for RNase protection assays were either raised in the dark from birth to P45 (P45 Dark-Reared; n = 1), received binocular TTX injections at P43 and were assayed at P45 (P45 Bin.TTX; n = 2), received binocular injections of sodium citrate vehicle solution at P43 and were assayed at P45 (P45 Bin.Cit.;n = 1), or were unmanipulated (P45 Normal; n = 2). Total RNA was extracted from primary visual cortex, frontal cortex, LGN, and superior colliculus and analyzed by RNase protection assays with a cat-specific32P-labeled BDNF riboprobe (top band). A cat-specific GAPDH riboprobe (bottom band) was used in the same hybridization mixture as an internal control for RNA quantification. Protected fragments for BDNF and GAPDH (362 and 226 nucleotides, respectively) are indicated byasterisks. Each lane was loaded with total RNA from a single animal. The right-most four lanes contain control hybridizations using yeast tRNA and undigested probes for GAPDH and BDNF. MW, Molecular weight markers.