Fig. 5.
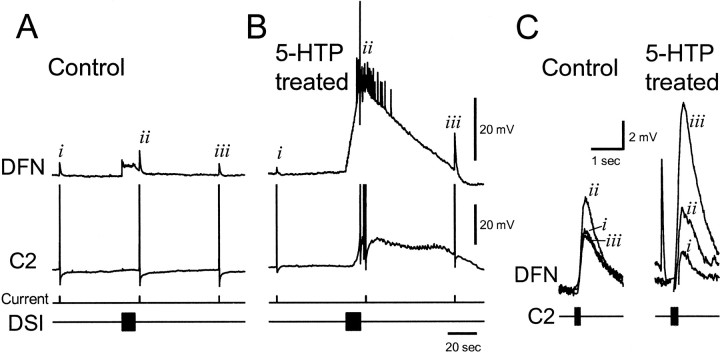
5-HTP treatment increases DSI neuromodulation of C2 synaptic strength. A, Under control conditions, DSI enhanced the C2-evoked summated EPSP in a dorsal flexion neuron, DFN, when C2 was stimulated 3 sec after the end of the AP train in DSI. But 60 sec after that, the EPSP was back to pre-DSI levels.B, After 5-HTP treatment (1 mm, 40 min, 24 hr before recording), an AP train in DSI evokes a much larger response in C2 and the DFN. The C2-evoked EPSP in DFN, while increased 3 sec after DSI stimulation (but not discernible in the midst of the myriad polysynaptic EPSPs and one truncated AP; however, see partC), is even larger 60 sec later. C,Faster timescale depictions of the summated C2-evoked EPSPs from the control and 5-HTP-treated recordings show the long-lasting modulation of C2 synaptic strength by DSI. The overlapped traces from control and 5-HTP-treated conditions correspond to the summated EPSPs, denoted byi, ii, and iii inA and B, respectively. The summated EPSPs have been baseline- adjusted for comparison. The additional fast EPSP in the 5-HTP-treated group immediately preceded summated EPSPii (from B) and originated from some cell other than the C2 or DSI. For both control and 5-HTP-treated conditions, the DSI was stimulated at 2 Hz for 10 sec. The C2 was stimulated to fire four APs at 20 Hz for the control and five APs after 5-HTP treatment. The number of APs fired by C2 was increased to facilitate measurement of the summated EPSP.