Fig. 4.
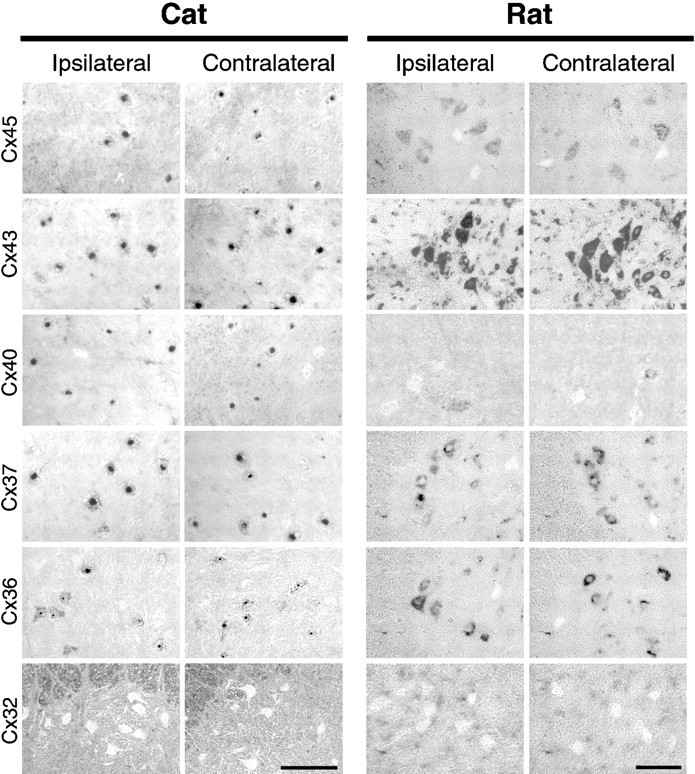
Connexin expression in motor neurons analyzed byin situ hybridization in rat and cat spinal cord is unchanged after axotomy. To compare the pattern of connexin expression between normal and axotomized rat motor neurons with normal and axotomized cat motor neurons in which extensive dye coupling had been characterized, in situ hybridization was performed with rat connexin cRNA probes and was visualized with a chromogenic reaction that resulted in positive cells appearing dark. Left, Shown are photographs of cat ventral L6–L7 spinal cord containing the gastrocnemius–soleus motor pools ipsilateral (left) or contralateral (left middle) to muscle nerve cut 4 weeks previously. Scale bar, 500 μm. Right, Shown are photographs of the lateral region of rat ventral spinal cord containing the sciatic nerve motor pools ipsilateral (right middle) or contralateral (right) to sciatic nerve cut 1 week previously. Cx45, Cx43, Cx40, Cx37, and Cx36 mRNA were detected in cat and rat motor neurons, identified by their location and large soma size. The pattern observed with each connexin probe after in situ hybridization in cat spinal cord was similar to that observed in rat for each experimental condition, with the exception that Cx40 was expressed in ∼10% of rat motor neurons compared with ∼75% of cat motor neurons. Neither Cx32 (bottom) or Cx26 (data not shown) were detected in motor neurons, but these were detected in meningeal and ependymal cells and glia. Scale bar, 100 μm.
