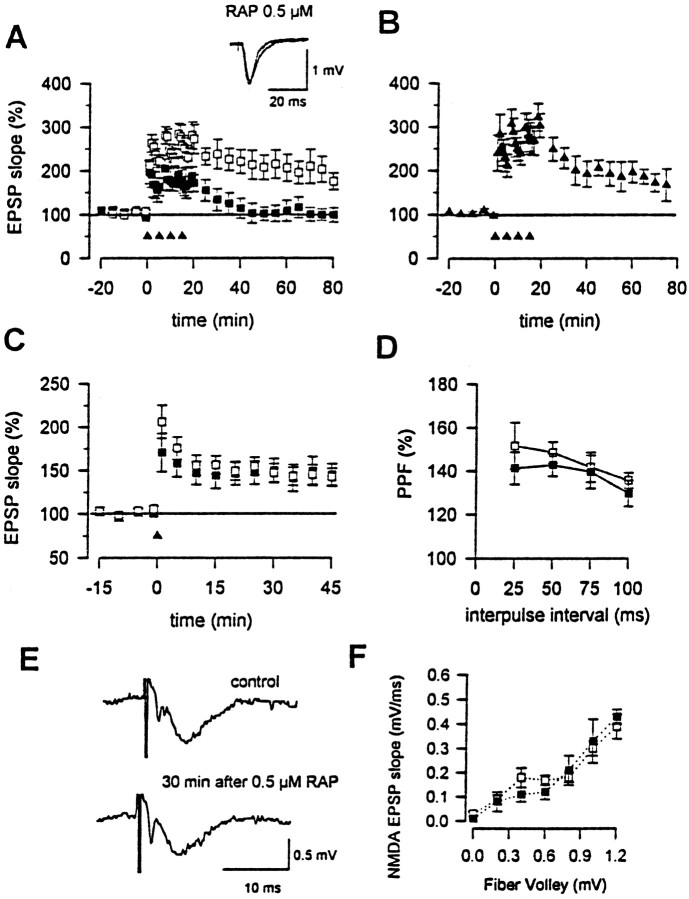
Fig. 1.
LRP is important for hippocampal L-LTP.A, L-LTP is abolished by RAP pretreatment (0.5 μm, closed squares). L-LTP recorded with buffer alone is shown with open squares. Four-train stimulation is marked with arrowheads.Inset, Traces of EPSPs indicating that 40 min after the induction of L-LTP, hippocampal potentials with RAP treatment have returned to those of baseline. B, RAP at a lower concentration (50 nm) produces a smaller inhibition.C, RAP (0.5 μm, closed squares) does not affect E-LTP induced by one-train stimulation. E-LTP recorded with buffer alone is shown with open squares. D, Synaptic responses to a paired-pulse stimulation at different intervals (25, 50, 75, and 100 msec) are not affected by RAP (0.5 μm, closed squares).Open squares are recordings with buffer alone.E, RAP does not affect NMDA receptor-mediated EPSPs.F, The input-output curves of NMDA receptor-mediated EPSPs in control medium (open squares) and medium containing RAP (0.5 μm, closed squares).