Fig. 4.
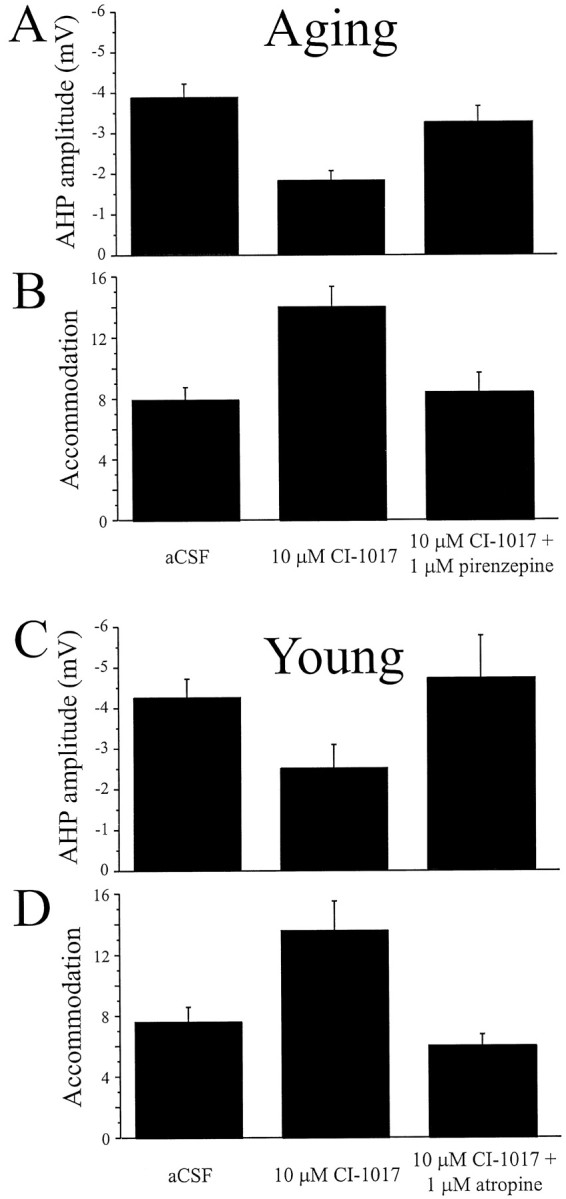
CI-1017 increased the excitability of both young and aging hippocampal pyramidal neurons by significantly reducing the amplitude of the AHP and spike-frequency adaptation. A, CI-1017 (10 μm) significantly reduced the mean amplitude of the AHP in neurons from aging rabbits, and the effect was significantly reversed after application of the m1-specific antagonist pirenzepine (1 μm). B, CI-1017 significantly reduced the spike-frequency adaptation of neurons from aging rabbits after application of the drug (10 μm) to the bath; the effect was significantly reversed by the addition of pirenzepine (1 μm). C, CI-1017 (10 μm) reduced the mean amplitude of the AHP in neurons from young rabbits; the effect was reversed after application of the cholinergic antagonist atropine (1 μm). D, CI-1017 (10 μm) significantly reduced the spike-frequency adaptation of neurons from young rabbits; the effect was significantly reversed by the addition of atropine (1 μm).
