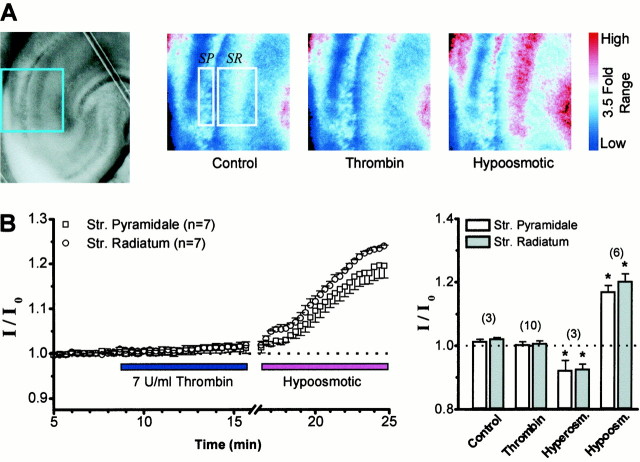
Fig. 2.
A, Left panel, Photograph of a 300 μm rat hippocampal slice with the region indicated in blue expanded to theright. Right panels, Pseudocolor representation of the relative intensity of transmitted light (500–550 nm) in a slice bathed in ACSF after treatment with 0.5 μmTTX (Control), 0.5 μm TTX plus 7 U/ml thrombin, or 0.5 μm TTX with ACSF made hypo-osmotic by addition of 10% v/v water. Boxes show regions from which average intensity measurements were made in this slice.SP, Stratum pyramidale; SR, stratum radiatum. The color code on the rightindicates a 3.5-fold relative range of intensity. B,Left panel, Mean time course (±SEM) of the effects of thrombin or hypo-osmotic treatment on transmitted light in seven cells. Increased transmittance is correlated with reduced extracellular volume fraction (see Results) (Andrew and MacVicar, 1994). Right panel, Summary of experiments showing no effect of thrombin on mean relative transmitted light compared with hypo-osmotic ACSF or ACSF made hyperosmotic by addition of 30 mm mannitol.Bars show the mean ratio of transmittance after treatment (I) to control transmittance (I0).* indicates significantly different from control measurements (p < 0.05; ttest). The number of slices is indicated inparentheses.