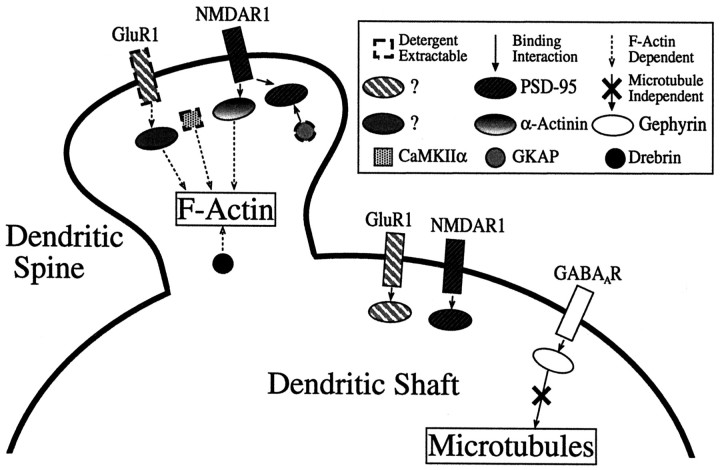
Fig. 8.
Diagrammatic summary of results. Two different AMPA receptor-binding proteins are postulated to account for the differential detergent extractability and actin dependence of AMPA receptors in spines versus shaft synapses as reported previously (Allison et al., 1998); these may correspond to different forms of GRIP and/or PICK1. The proteins dependent on F-actin for clustering include α-actinin-2, drebrin, CaMKIIα, and AMPAR in spines. GKAP and CaMKIIα are partially detergent extractable, and AMPAR is highly extractable only from spine synapses. All synaptic components were found to be localized independent of microtubules; this is emphasized in the diagram for gephyrin and GABAAR. These results indicate different modes of localization for different components of dendritic spines and suggest that PSD-95 and gephyrin form part of core scaffolds of excitatory and inhibitory synapses maintained independent of association with conventional cytoskeletal systems.