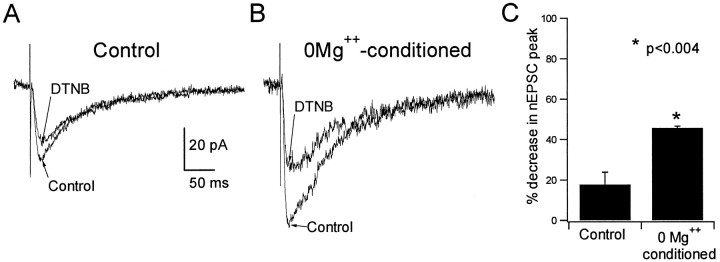
Fig. 5.
NMDAR-mediated synaptic currents were more sensitive to inhibition by DTNB after ictal activity.A, Shown superimposed are averaged (4–6 events) NMDAR-mediated EPSCs recorded at a holding potential of −15 mV in a CA1 neuron from a control slice before and after exposure to 500 μm DTNB. B, The same is shown for a neuron recorded from a slice that had been exposed to Mg2+-free media and exhibited spontaneous field activity for 30 min before the initiation of whole-cell recording (see Materials and Methods). C, The bar graphs show summary data. The increased sensitivity of NMDAR-mediated EPSCs to DTNB-induced inhibition indicated that the epileptogenic condition had caused NMDAR redox sites to be reduced by endogenous factors.