Fig. 4.
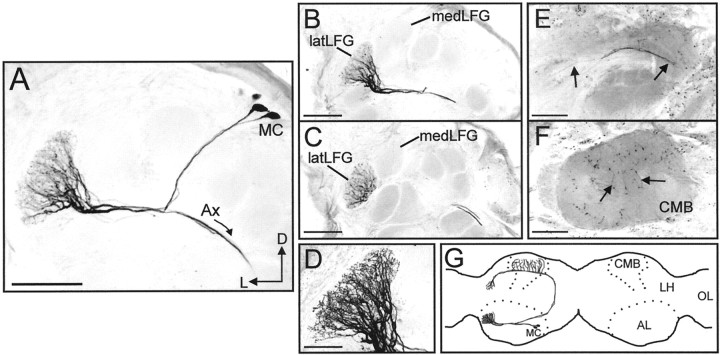
Morphology of uniglomerular PNs arborizing within the latLFG. A, Confocal stack collected from a whole-mount preparation, showing PNs with somata in the medial group of neuronal cell bodies (MC), dendritic arborizations restricted to the latLFG, and axons (Ax) projecting from the antennal lobe (AL). B,C, Confocal images collected from the same preparation shown in A after sectioning, illustrating more clearly the close anatomical relationship between the medLFG and latLFG. The dendritic arborizations of these PNs were restricted to the latLFG. Somata are not visible in either section. D, High magnification (60×) confocal stack of the latLFG shown inB. The fine dendritic arborizations of these PNs were highly branched and extended throughout the entire glomerulus.E, F, Axonal projection patterns of these latLFG-PNs. Axons (arrows in E) projected through the inner antennocerebral tract to the calyces of the ipsilateral mushroom body (CMB) and the lateral horn of the protocerebrum. Axon terminals are visible in the CMB indicated inF by arrows. G, Schematic illustration (horizontal view) showing the general morphology of latLFG-PNs. All latLFG-PNs observed to date shared the same basic morphology and are classified as type PIa neurons (Homberg et al., 1988). LH, Lateral horn of the protocerebrum;OL, optic lobe; D, dorsal;L, lateral. Dotted lines indicate the outlines of the ALs and the mushroom bodies. Scale bars:A–C, E, F, 100 μm; D, 50 μm. All images were inverted using Corel Photo-Paint.