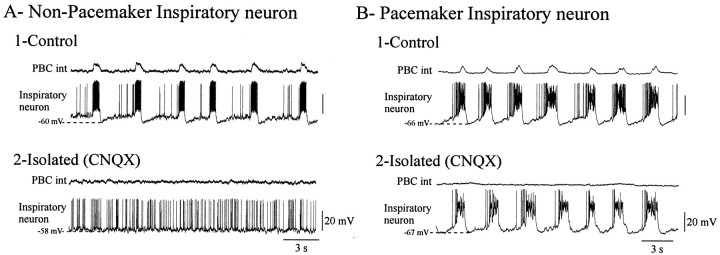
Fig. 5.
Blockade of respiratory network activity reveals non-pacemaker and pacemaker inspiratory neurons. A1,B1, Two examples of inspiratory neurons recorded simultaneously with integrated population activity from the PBC in control conditions. A2, B2, After elimination of network activity by blocking glutamatergic synaptic transmission with CNQX (20 μm), the non-pacemaker neuron became tonically active (A2), whereas pacemaker neuron remained rhythmically active (B2). Recordings were obtained from P9 and P7 animals, respectively.