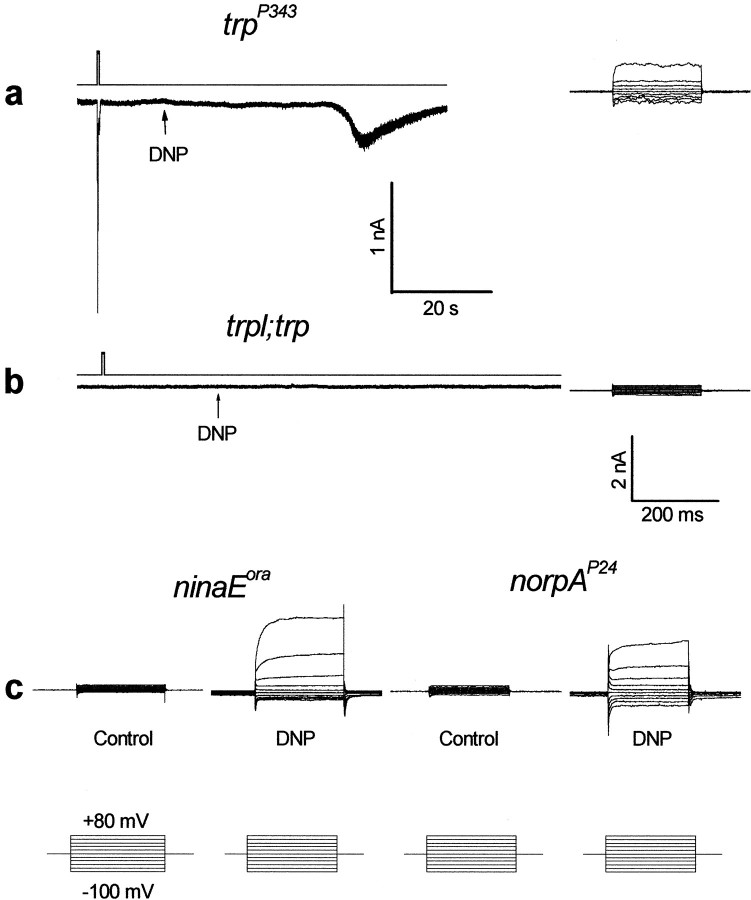
Fig. 8.
The effects of DNP on Drosophilamutants. a, A relatively slow induction of a small and noisy inward current in the dark was observed intrpP343 after application of 0.1 mm DNP (arrow) during recordings without ATP and NAD in the pipette. Inward currents could not be induced without application of DNP under similar recording conditions. The right traces show a family of current traces elicited by a series of voltage steps as in Figure 7c at 1.5 mmexternal Ca2+. Similar families of current traces of similar amplitudes were observed at 0 Ca2+ medium (n = 3). b, Recording from thetrpl302;trpP343double mutant using pipettes in which ATP and NAD were omitted and 0.1 mm DNP was applied to the external medium as indicated. No dark inward current was observed even 16 min after the beginning of whole-cell recordings. The right traces show a family of current traces elicited by a series of voltage steps as in Figure7c at 1.5 mm external Ca2+. Similar results were obtained from four different cells in which DNP was included in the recording pipette. Note that neither light-induced currents nor inward currents in the dark could be induced in the double mutant. c, The effects of DNP (applied through the pipette) on theninaEora, Gαq1, andnorpAP24 mutants. Thetraces are families of current traces elicited by a series of voltage steps as in Figure 7c at 1.5 mm external Ca2+. The typical TRP-dependent current is observed only in cells in which the recording pipette included 0.1 mm DNP but not in control cells of the same retinae, as indicated. Similar results were obtained from three to six different cells of each mutant. The traces recorded from theGαq1 mutant are not shown. The lower calibration applies to all families of current traces elicited by a series of voltage steps.