Fig. 2.
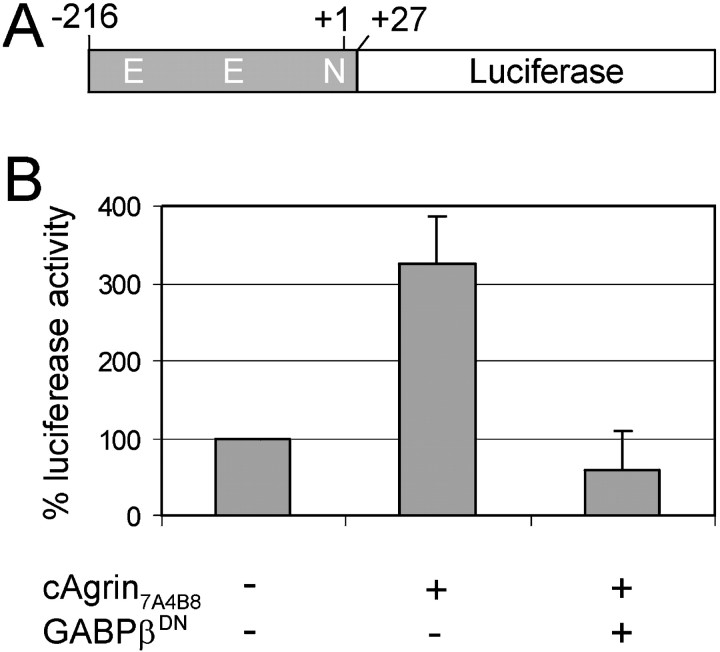
Agrin induces the expression of an AChRε subunit reporter construct via a GABP-dependent mechanism in vivo. A, Diagram of the AChRε subunit reporter construct used in this study. A fragment of the ε subunit gene (gray) extending 216 bp upstream from the transcription start site drives the expression of a luciferase gene. This fragment contains two E-boxes (E), putative binding sites for basic helix-loop-helix myogenic factors, and one N-box (N). B, In each individual experiment, luciferase activity of the AChRε reporter construct injected alone was set as 100% (first column). Coinjection of expression constructs encoding full-length neural agrin (cAgrin7A4B8) increases luciferase activity more than threefold (second column; p < 0.01). This increase is abolished by expression of the dominant-negative mutant of GABPβ (third column;p < 0.01). Data represent mean ± SDs of three independent injections (3 injected rats). Note that, in each individual injection, luciferase activity was normalized to the β-galactosidase activity derived from the coinjected NLS-LacF construct. The effect of neural agrin and GABPβDN is specific for the AChRε promoter because a muscle creatine kinase promoter construct was not affected by either condition (reporter alone, 100%; reporter plus cAgrin7A4B8, 88.3%; reporter plus cAgrin7A4B8 plus GABPβDN, 87.2%).