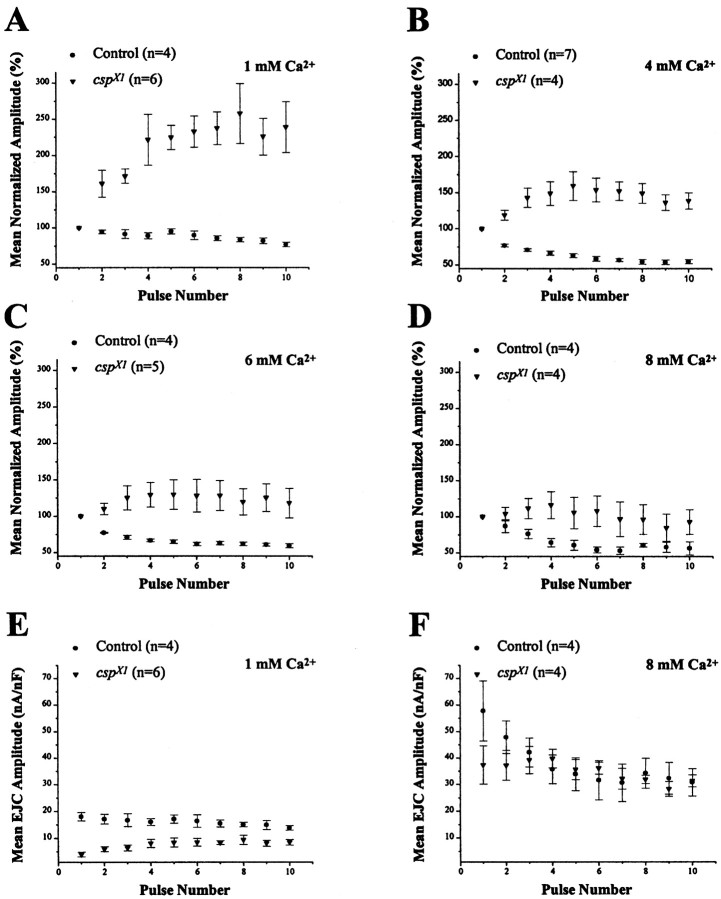
Fig. 3.
Facilitation of transmission at cspmutant neuromuscular junctions. Postsynaptic responses at 23°C incsp null mutants show facilitation of evoked neurotransmitter release under conditions in which control responses show a depression. EJCs at Drosophila larval NMJs were recorded under two-electrode voltage clamp at different [Ca2+]e while stimulating the motor nerve at 30 Hz. Symbols represent mean EJC amplitudes normalized to the first response. Error bars indicate SEM.A, In 1 mm, pronounced facilitation occurs in the cspX1 null mutant. Normalized mutant amplitudes measured for pulses 2–10 are significantly different from control (p < 0.02, Student'st test). B, At 4 mmCa2+, facilitation of mutant responses is reduced compared with the results obtained in 1 mmCa2+, and all responses are significantly different from control (p < 0.02, Student's ttest). C, Facilitation of csp mutant responses is further reduced in 6 mmCa2+ (p < 0.02, Student'st test). D, In 8 mmCa2+, facilitation of csp mutant responses becomes negligible, because none of the subsequent mutant responses (2–10) is significantly different from controls (p > 0.06, Student's t test).E, Absolute EJC amplitudes in 1 mmCa2+ normalized for muscle size by dividing the current amplitude by the cell capacitance. All mutant EJC amplitudes in 1 mm Ca2+ are significantly different from control (p < 0.04, Student's ttest). F, Absolute EJC amplitudes in 8 mmCa2+. None of the mutant EJC amplitudes are significantly different from control (p > 0.1, Student's t test).