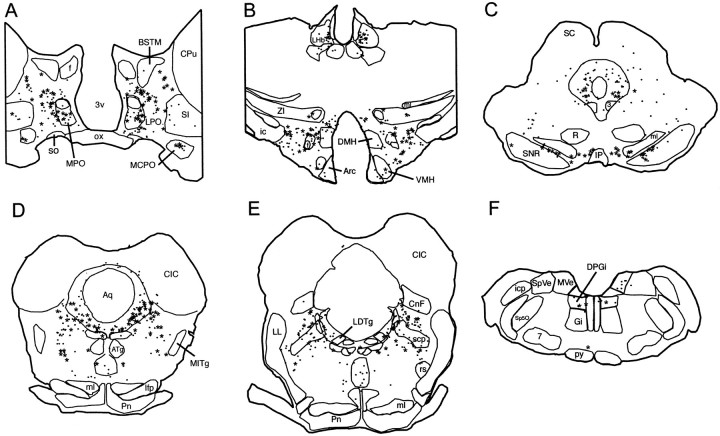
Fig. 8.
Schematic representation of the GABAergic afferents to the DRN from rostral to caudal levels. Drawings of 20 μm frontal sections are shown. Each point corresponds to a retrogradely labeled cell (CTb+), and each starcorresponds to a double-labeled cell (CTb+/GAD+). 3, Oculomotor nucleus; 7, facial nucleus;3V, third ventricle; Arc, arcuate nucleus; ATg, anterior tegmental nucleus;Aq, aqueduct; BSTM, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, medial division; CIC, central nucleus of the inferior colliculus; CG, central gray;CNf, cuneiform nucleus; CPu, caudate putamen; DMH, dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus;DPGi, dorsal paragigantocellular nucleus;f, fornix; ic, internal capsule;icp, inferior cerebellar peduncle; IP, interpeduncular nucleus; LDTg, laterodorsal tegmental nucleus; lfp, longitudinal fasciculus of the pons;LHb, lateral habenular nucleus; LL, lateral lemniscus; LPO, lateral preoptic area;ml, medial lemniscus; MCPO, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; MITg, microcellular tegmental nucleus;MPO, medial preoptic nucleus; MVe, medial vestibular nucleus; ox, optic chiasm; Pn, pontine nuclei; Py, pyramidal tract, R, red nucleus; rs, rubrospinal tract; SC, superior colliculus; scp, superior cerebellar peduncle;SI, substantia innominata; SNR, substantia nigra, reticulata; SO, supraoptic nucleus;Sp5O, spinal 5 nucleus, oral part; SpVe, spinal vestibular nucleus; ZI, zona incerta.