Fig. 2.
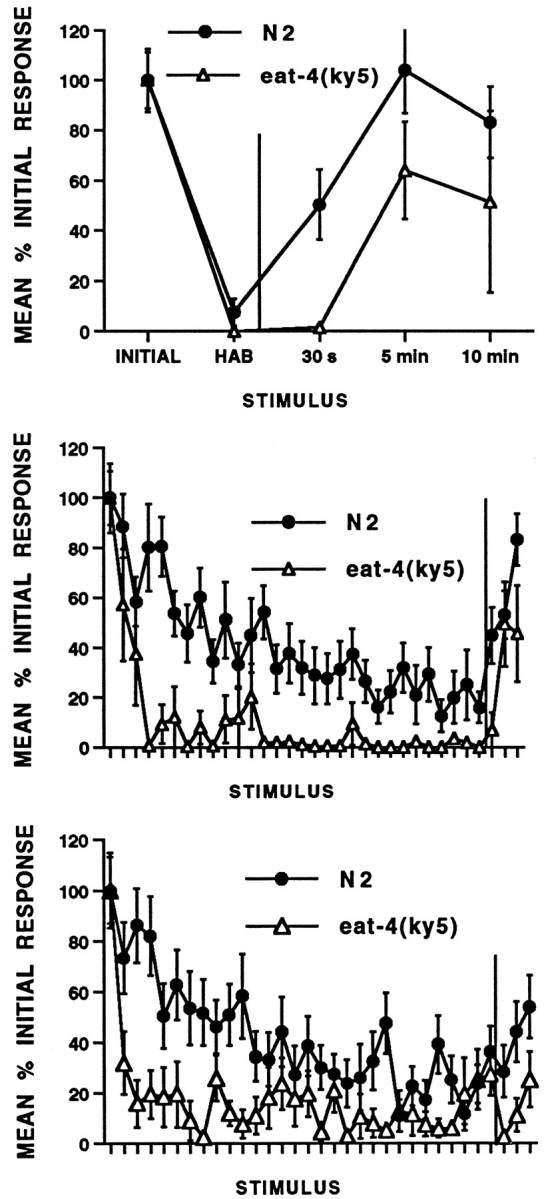
Habituation and spontaneous recovery from habituation for wild-type N2 and eat-4 worms. All ISI worms received 30 stimuli followed by recovery tests at 30 sec, 5 min, and 10 min after habituation (n = 20 per group). At each ISI, habituation was more rapid and complete and recovery slower in eat-4 worms than in wild-type worms.Top, Two-second ISI: mean standardized reversal magnitude (in pixels) for responses to 30 tap stimuli and three recovery tests (after the vertical line; 30 sec, 5 min, and 10 min). eat-4 worms show habituation and rapid but incomplete recovery from habituation. Middle, Ten-second ISI: eat-4 worms show more rapid and complete habituation and slower recovery (after the vertical line) from habituation than wild-type worms.Bottom, Sixty-second ISI: eat-4 worms show more rapid and complete habituation and slower recovery (after thevertical line) from habituation than wild-type worms.
